AG Krey
Research summary
Our research is focused on structural studies in order to understand molecular mechanisms that are essential for various steps of the virus cycle.
Our major goals are:
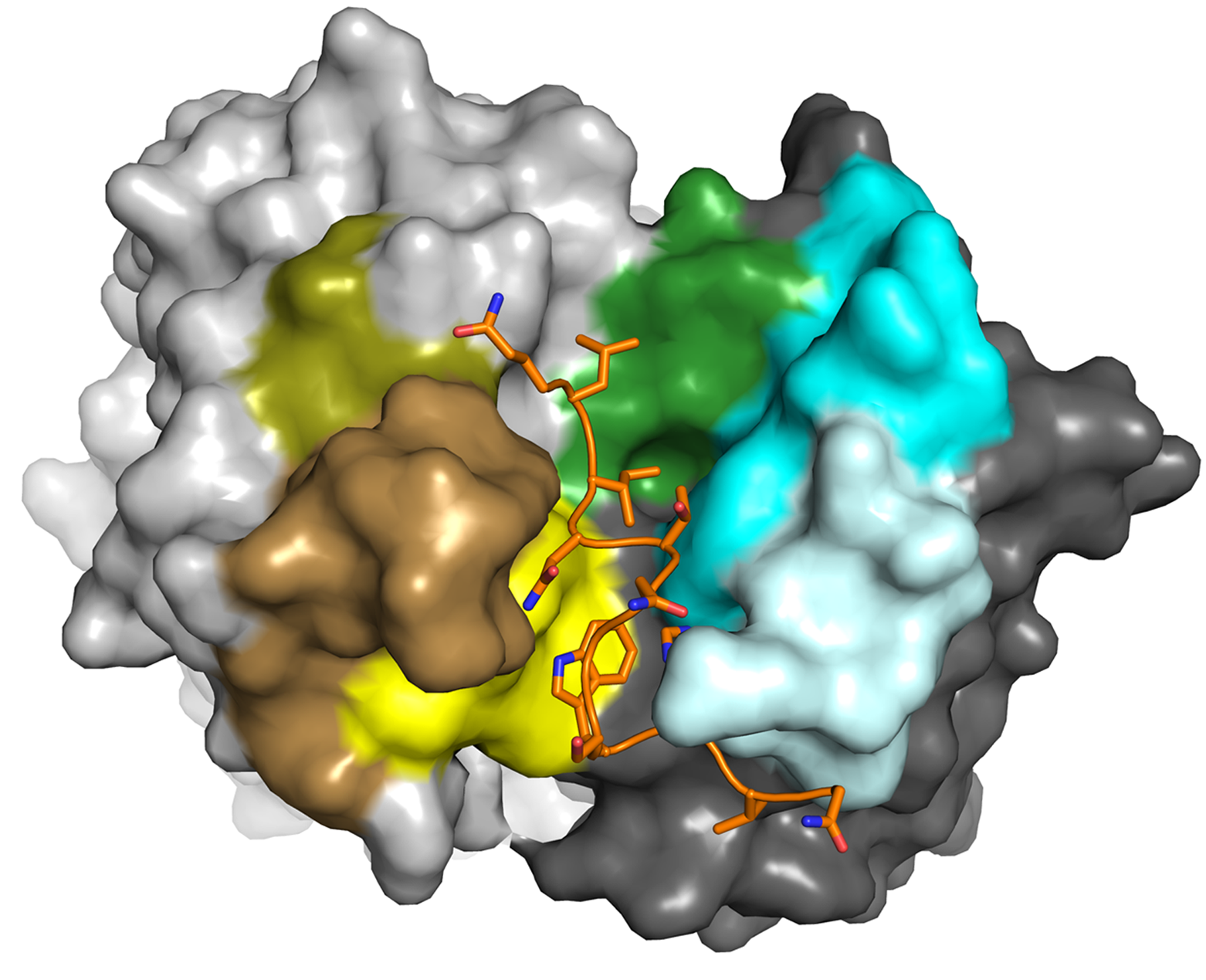
- Structural characterization of virus glycoproteins involved in membrane fusion and interactions with the immune system and identification of the determinants of an efficient neutralizing antibody response to facilitate informed vaccine design. During the last years we have contributed the structures of a number of neutralizing epitopes recognized by neutralizing antibodies within the major glycoprotein E2 of the hepatitis C virus (HCV). Based on these structures we concluded that the binding site for the cellular receptor CD81 - representing the major target of neutralizing antibodies - is conformationally flexible. This conformational flexibility likely constitutes a novel strategy that HCV utilizes to evade potently neutralizing antibodies.
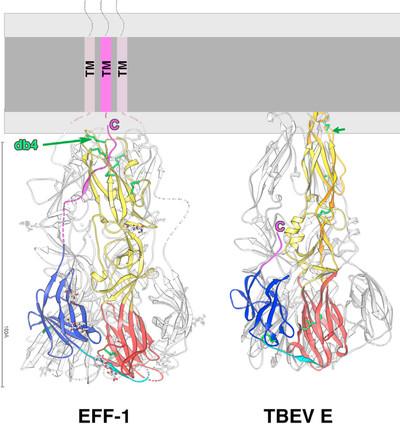
- The recent structural characterization of the C. elegans cell fusion protein EFF-1 revealed that certain effector proteins driving virus-cell fusion and cell-cell fusion are structurally homologous and also share mechanistic similarities. We are currently evaluating, whether - in addition to the structural homology of the effector proteins - both processes also share other common features or key players.
- More recently we also started to investigate the mechanism-of-action leading to the assembly and disassembly of large viral capsids, an essential step for the production of virus progeny as well as for the release of the viral genome during virus entry.
We study mostly viruses that constitute a global public health and/or veterinary concern and use structural biology/biophysical methods with a special focus on X-ray crystallography. The structural knowledge gained from our experiments can be used for structure-based design of preventive or curative antiviral agents, i.e., this knowledge has a direct potential for translational medicine. Furthermore, structural studies are often performed in parallel on homologous proteins from related viruses, which provides crucial information about the evolutionary relationship between these viruses and allows the identification of conserved features and/or pathways, which often are the most promising drug targets.
Group members

Team leader
- Prof. Dr. Thomas Krey
Medizinische Hochschule Hannover (Hannover Medical School)
Institute of Virology, OE5230
Carl-Neuberg-Str. 1
30625 Hannover
Phone +49-451-3101-3100
Departmental Secretary +49 511 532 6736
FAX +49 511 532 8736
Email Krey.Thomas@MH-Hannover.de
Publications in peer-reviewed journals, Reviews, Book chapters, Comments etc.
Selected Publications:
Fedry J, Forcina J, Legrand P, Pehau-Arnaudet G, Haouz A, Johnson M, Rey FA, Krey T. 2018. Evolutionary diversification of the HAP2 membrane insertion motifs to drive gamete fusion across eukaryotes. PLoS biology 16:e2006357.
Ströh LJ, Nagarathinam K, Krey T. 2018. Conformational Flexibility in the CD81-Binding Site of the Hepatitis C Virus Glycoprotein E2. Frontiers in immunology 9:1396.
Lodermeyer V, Ssebyatika G, Passos V, Ponnurangam A, Malassa A, Ewald E, Stürzel CM, Kirchhoff F, Rotger M, Falk CS, Telenti A, Krey T, Goffinet C. 2018. The Antiviral Activity of the Cellular Glycoprotein LGALS3BP/90K Is Species Specific. Journal of Virology 92.
Klingen TR, Reimering S, Loers J, Mooren K, Klawonn F, Krey T, Gabriel G, McHardy AC. 2018. Sweep Dynamics (SD) plots: Computational identification of selective sweeps to monitor the adaptation of influenza A viruses. Scientific reports 8:373.
Riitho V, Walters AA, Somavarapu S, Lamp B, Rümenapf T, Krey T, Rey FA, Oviedo-Orta E, Stewart GR, Locker N, Steinbach F, Graham SP. 2017. Design and evaluation of the immunogenicity and efficacy of a biomimetic particulate formulation of viral antigens. Scientific reports 7:97.
Vasiliauskaite I, Owsianka AM, England P, Khan AG, Cole S, Bankwitz D, Foung SKH, Pietschmann T, Marcotrigiano J, Rey FA, Patel AH, Krey T. 2017. Conformational Flexibility in the Immunoglobulin-Like Domain of the Hepatitis C Virus Glycoprotein E2. mBio 8:e00382-00317.
González-Motos V, Jürgens C, Ritter B, Kropp KA, Durán V, Larsen O, Binz A, Ouwendijk WJD, Lenac Roviš T, Jonjić S, Verjans GMGM, Sodeik B, Krey T, Bauerfeind R, Schulz TF, Kaufer BB, Kalinke U, Proudfoot AEI, Rosenkilde MM, Viejo-Borbolla A. 2017. Varicella zoster virus glycoprotein C increases chemokine-mediated leukocyte migration. PLoS pathogens 13:e1006346.
Fedry J, Liu Y, Pehau-Arnaudet G, Pei J, Li W, Tortorici MA, Traincard F, Meola A, Bricogne G, Grishin NV, Snell WJ, Rey FA, Krey T. 2017. The Ancient Gamete Fusogen HAP2 Is a Eukaryotic Class II Fusion Protein. Cell 168:904-915.e910.
Cowton VM, Angus AGN, Cole SJ, Markopoulou CK, Owsianka AM, Dunlop JI, Gardner DE, Krey T, Patel AH. 2016. Role of Conserved E2 Residue W420 in Receptor Binding and Hepatitis C Virus Infection. Journal of Virology 90:7456-7468.
Backovic, M., and T. Krey. 2016. Stable Drosophila Cell Lines: An Alternative Approach to Exogenous Protein Expression. In D. W. Murhammer (ed.), Baculovirus and Insect Cell Expression Protocols. Humana Press, Totowa, N.J.
Callens N, Brügger B, Bonnafous P, Drobecq H, Gerl MJ, Krey T, Roman-Sosa G, Rümenapf T, Lambert O, Dubuisson J, Rouillé Y. 2016. Morphology and Molecular Composition of Purified Bovine Viral Diarrhea Virus Envelope. PLoS pathogens 12:e1005476.
Keck ZY, Girard-Blanc C, Wang W, Lau P, Zuiani A, Rey FA, Krey T, Diamond MS, Foung SK. 2016. Antibody response to the hypervariable region-1 interferes with broadly neutralizing antibodies to hepatitis C virus. J Virol doi:10.1128/JVI.02458-15.
Urbanowicz RA, McClure CP, Brown RJ, Tsoleridis T, Persson MA, Krey T, Irving WL, Ball JK, Tarr AW. 2015. A diverse panel of Hepatitis C Virus glycoproteins for use in vaccine research reveals extremes of monoclonal antibody neutralization resistance. J Virol doi:10.1128/JVI.02700-15.
Marnata C, Saulnier A, Mompelat D, Krey T, Cohen L, Boukadida C, Warter L, Fresquet J, Vasiliauskaite I, Escriou N, Cosset FL, Rey FA, Lanford RE, Karayiannis P, Rose NJ, Lavillette D, Martin A. 2015. Determinants Involved in Hepatitis C Virus and GB Virus B Primate Host Restriction. J Virol 89:12131-12144.
Caval V, Bouzidi MS, Suspene R, Laude H, Dumargne MC, Bashamboo A, Krey T, Vartanian JP, Wain-Hobson S. 2015. Molecular basis of the attenuated phenotype of human APOBEC3B DNA mutator enzyme. Nucleic Acids Res 43:9340-9349.
Meola A, Tarr AW, England P, Meredith LW, McClure CP, Foung SK, McKeating JA, Ball JK, Rey FA, Krey T. 2015. Structural flexibility of a conserved antigenic region in hepatitis C virus glycoprotein E2 recognized by broadly neutralizing antibodies. J Virol 89:2170-2181.
Meola A, Deville C, Jeffers SA, Guardado-Calvo P, Vasiliauskaite I, Sizun C, Girard-Blanc C, Malosse C, van Heijenoort C, Chamot-Rooke J, Krey T, Guittet E, Pêtres S, Rey FA, Bontems F. 2014. Robust and low cost uniform (15)N-labeling of proteins expressed in Drosophila S2 cells and Spodoptera frugiperda Sf9 cells for NMR applications. Journal of structural biology.
Pérez-Vargas, J., T. Krey, C. Valansi, O. Avinoam, A. Haouz, M. Jamin, H. Raveh-Barak, B. Podbilewicz, and F. A. Rey. 2014. Structural basis of eukaryotic cell-cell fusion. Cell. 157:407-419. J. P.-V. and T.K. contributed equally to this work.
Rey, F., B. Podbilewicz, J. Pérez-Vargas, and T. Krey. 2013. Class II Membrane Fusion Proteins in Viral and Cellular Fusion Events. Biophysj 104:12a.
Tarr, A. W., P. Lafaye, L. Meredith, L. Damier-Piolle, R. A. Urbanowicz, A. Meola, J.-L. Jestin, R. J. P. Brown, J. A. Mckeating, F. A. Rey, J. K. Ball, and T. Krey. 2013. An alpaca nanobody inhibits hepatitis C virus entry and cell-to-cell transmission. Hepatology 58:932-939.
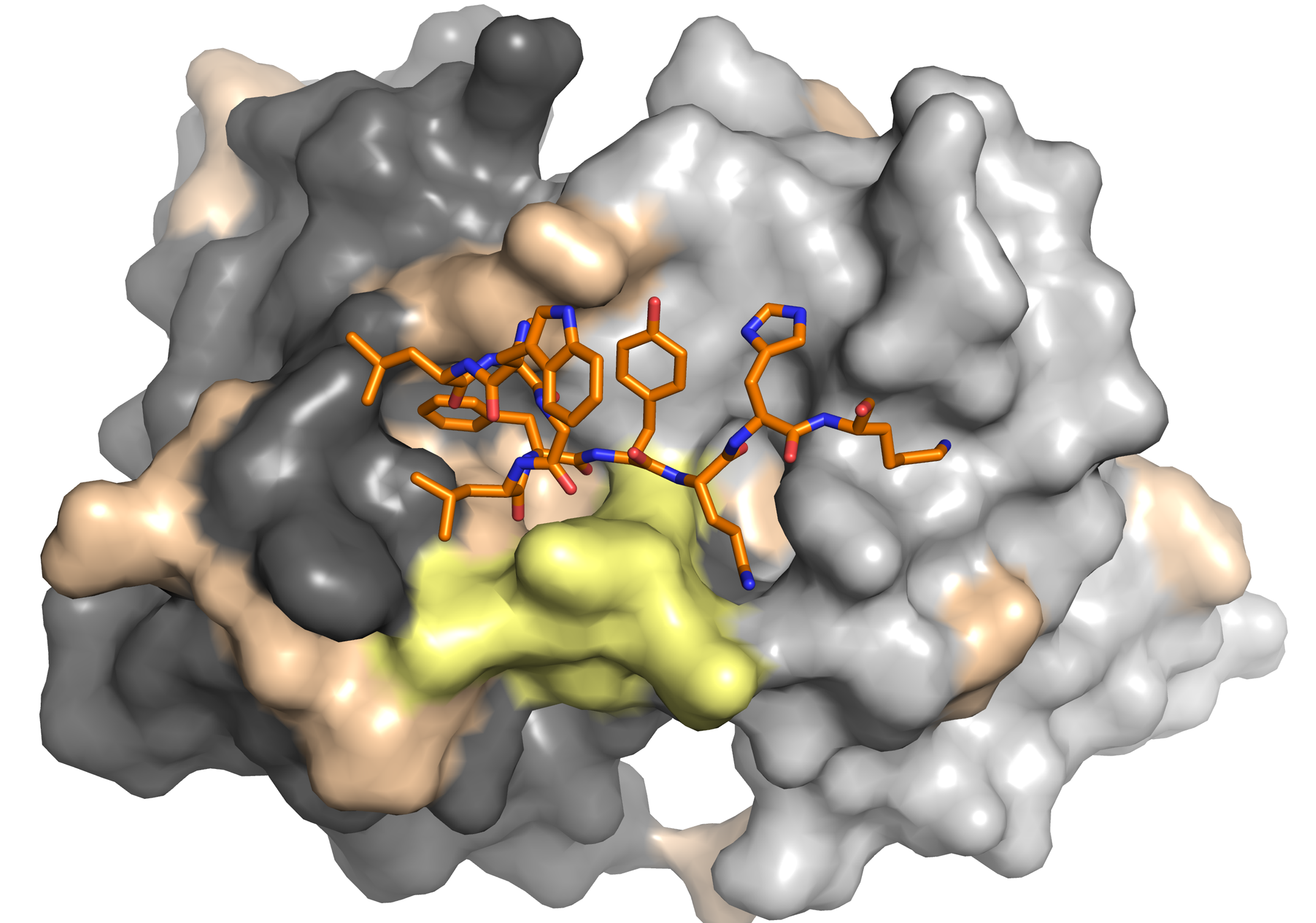
Krey, T., A. Meola, Z.-Y. Keck, L. Damier-Piolle, S. K. H. Foung, and F. A. Rey. 2013. Structural basis of HCV neutralization by human monoclonal antibodies resistant to viral neutralization escape. PLoS pathogens 9:e1003364.
DuBois, R. M., M.-C. Vaney, M. A. Tortorici, R. A. Kurdi, G. Barba-Spaeth, T. Krey, and F. A. Rey. 2013. Functional and evolutionary insight from the crystal structure of rubella virus protein E1. Nature 493:552-557.
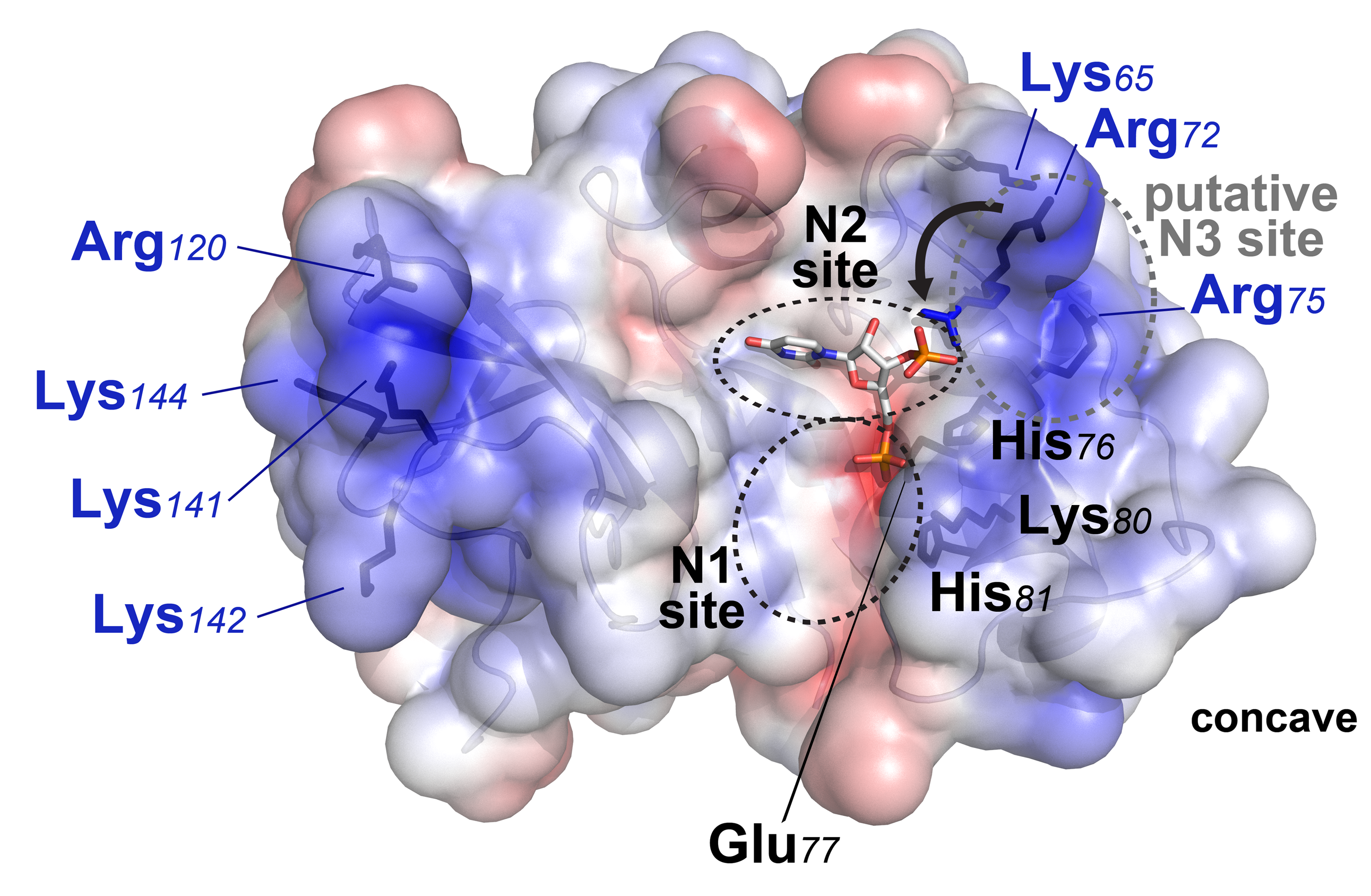
Krey, T., F. Bontems, C. Vonrhein, M. C. Vaney, G. Bricogne, T. Rumenapf, and F. A. Rey. 2012. Crystal Structure of the Pestivirus Envelope Glycoprotein E(rns) and Mechanistic Analysis of Its Ribonuclease Activity. Structure 20:862-73
Johansson, D. X., T. Krey, and O. Andersson. 2012. Production of Recombinant Antibodies in Drosophila melanogaster S2 Cells. In P. Chames (ed.), Antibody Engineering: methods and protocols. Humana Press, Totowa, N.J.
Keck, Z. Y., J. Xia, Y. Wang, W. Wang, T. Krey, J. Prentoe, T. Carlsen, A. Y. Li, A. H. Patel, S. M. Lemon, J. Bukh, F. A. Rey, and S. K. Foung. 2012. Human monoclonal antibodies to a novel cluster of conformational epitopes on HCV e2 with resistance to neutralization escape in a genotype 2a isolate. PLoS Pathog 8:e1002653.
Gilmartin, A. A., B. Lamp, T. Rumenapf, M. A. A. Persson, F. A. Rey, and T. Krey. 2011. High-level secretion of recombinant monomeric murine and human single-chain Fv antibodies from Drosophila S2 cells. Protein Eng Des Sel:1-8.
Rey FA, Pérez-Vargas J, Krey T, Podbilewicz B. 2011. The cell fusion proteins of the "FF" family are homologous to class II viral fusion proteins. Acta Crystallographica Section A 67:76-76
Albecka, A., R. Montserret, T. Krey, A. W. Tarr, E. Diesis, J. K. Ball, V. Descamps, G. Duverlie, F. Rey, F. Penin, and J. Dubuisson. 2011. Identification of new functional regions in hepatitis C virus envelope glycoprotein E2. J Virol 85:1777-92.
Gutsche, I., F. Coulibaly, J. E. Voss, J. Salmon, J. d'Alayer, M. Ermonval, E. Larquet, P. Charneau, T. Krey, F. Megret, E. Guittet, F. A. Rey, and M. Flamand. 2011. Secreted dengue virus nonstructural protein NS1 is an atypical barrel-shaped high-density lipoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:8003-8.
Keck, Z. Y., A. Saha, J. Xia, Y. Wang, P. Lau, T. Krey, F. A. Rey, and S. K. Foung. 2011. Mapping a Region of Hepatitis C Virus E2 That Is Responsible for Escape from Neutralizing Antibodies and a Core CD81-Binding Region That Does Not Tolerate Neutralization Escape Mutations. J Virol 85:10451-63.
2010:
Krey, T., J. d'Alayer, C. M. Kikuti, A. Saulnier, L. Damier-Piolle, I. Petitpas, D. X. Johansson, R. G. Tawar, B. Baron, B. Robert, P. England, M. A. Persson, A. Martin, and F. A. Rey. 2010. The disulfide bonds in glycoprotein E2 of hepatitis C virus reveal the tertiary organization of the molecule. PLoS Pathog 6:e1000762.
2006:
Krey, T., A. Himmelreich, M. Heimann, C. Menge, H. J. Thiel, K. Maurer, and T. Rumenapf. 2006. Function of bovine CD46 as a cellular receptor for bovine viral diarrhea virus is determined by complement control protein 1. J Virol 80:3912-22. T.K. and A.H. contributed equally to this work.
Krey, T., E. Moussay, H. J. Thiel, and T. Rumenapf. 2006. Role of the low-density lipoprotein receptor in entry of bovine viral diarrhea virus. J Virol 80:10862-7.
2005:
Krey, T., H. J. Thiel, and T. Rumenapf. 2005. Acid-resistant bovine pestivirus requires activation for pH-triggered fusion during entry. J Virol 79:4191-200.
2004:
Maurer, K., T. Krey, V. Moennig, H. J. Thiel, and T. Rumenapf. 2004. CD46 is a cellular receptor for bovine viral diarrhea virus. J Virol 78:1792-9.