PD Dr. Berislav Bošnjak

Institute of Immunology, OE 5240
I11-02-1120
Phone: +49 511 532 9729
E-Mail: Bosnjak.Berislav@mh-hannover.de
Research Focus
CD8 T cell functional diversity
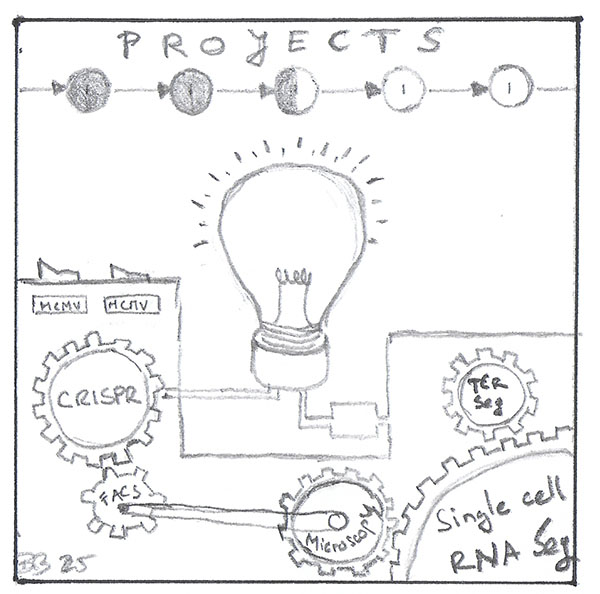
Cytotoxic CD8 T cells are part of a functional adaptive immune system crucial for intracellular pathogen elimination. They develop in the thymus, re-arranging the T-cell receptor (TCR) locus to create a unique clone-specific cell-surface TCR complex. Such naïve CD8 T cells leave the thymus and circulate through the blood, secondary lymphoid organs, and lymph until they encounter a specific peptide presented by antigen-presenting cells in the context of MHC class I molecules. Antigen recognition leads to CD8 T cell activation, proliferation, and differentiation into effector CD8 T cells that efficiently eliminate infected cells and protect the host from severe infection. After pathogen eradication, the pathogen-specific effector CD8 T cell population contracts to a fraction of memory cells that survive in the organism for years, ensuring a rapid and robust immune response upon pathogen re-counter. All CD8 T cell differentiation stages are phenotypically and functionally heterogeneous, and their composition is influenced by donor age and a person’s history of pathogen encounters.
To understand the functional diversity of CD8 T cell populations, we investigate their role in viral infections and transplantation. As a model viral pathogen, we use cytomegalovirus (CMV), a large DNA virus of the beta herpesvirus family. CMV evolved immune escape mechanisms, allowing the virus to establish persistent and then latent infection throughout the host's lifetime. During latency, in cooperation with other leukocytes, CD8 T cells actively suppress CMV reactivation. Populations with immature, senescent, or compromised immune systems, such as infants, older individuals, and transplant patients, are especially vulnerable to CMV infection or reactivation. We aim to understand the functional diversity of CMV-specific CD8 T cells using human samples and mouse models. We also use mouse models to investigate CMV tropism and dissemination. Additionally, we focus on the role of CD8 T cells in alloreactive immune responses, which mediate the rejection of transplanted organs.
Open Position
Open Position
Master Thesis: "Unraveling mechanisms of CD8+ T cell-mediated allogenicity in the liver"