Research report 2015
Cover picture:
The cover image/animation of the 2015 research report shows an animation with the in vitro uptake of 30-100 nM sized exosomes in cardiomyocytes.
Exosomes are a type of vesicle and are responsible for paracrine communication pathways in the heart (Bang et al., JCI, 2014). In particular, the pathway of exosomes from fibroblasts to neighboring cardiomyocytes is of great importance. Exosomes packed with microRNAs (class of non-coding RNAs) can trigger pathological size growth in cardiomyocytes.
In the animation shown here, exosomes were isolated from a fibroblast culture via several centrifugation steps, PKH26-stained and incubated with neonatal rat cardiomyocytes for 2 hours. The cells were then fixed, cardiomyocytes were stained with WGA (wheat germ agglutinin) Alexa Fluor 488 and confocal microscopy was performed. In the animation, cardiomyocytes are stained green (membrane staining), fibroblast exosomes are stained red and the cell nuclei are stained blue (DAPI).
The animation was provided by Prof. Dr. Dr. Thomas Thum, Director of the Institute of Molecular and Translational Therapy Strategies (IMTTS, IFB-Tx).
The imaging of the cell was carried out in close collaboration with Prof. Dr. Dr. Evgeni Ponimaskin from the Institute of Neurophysiology at the MHH.
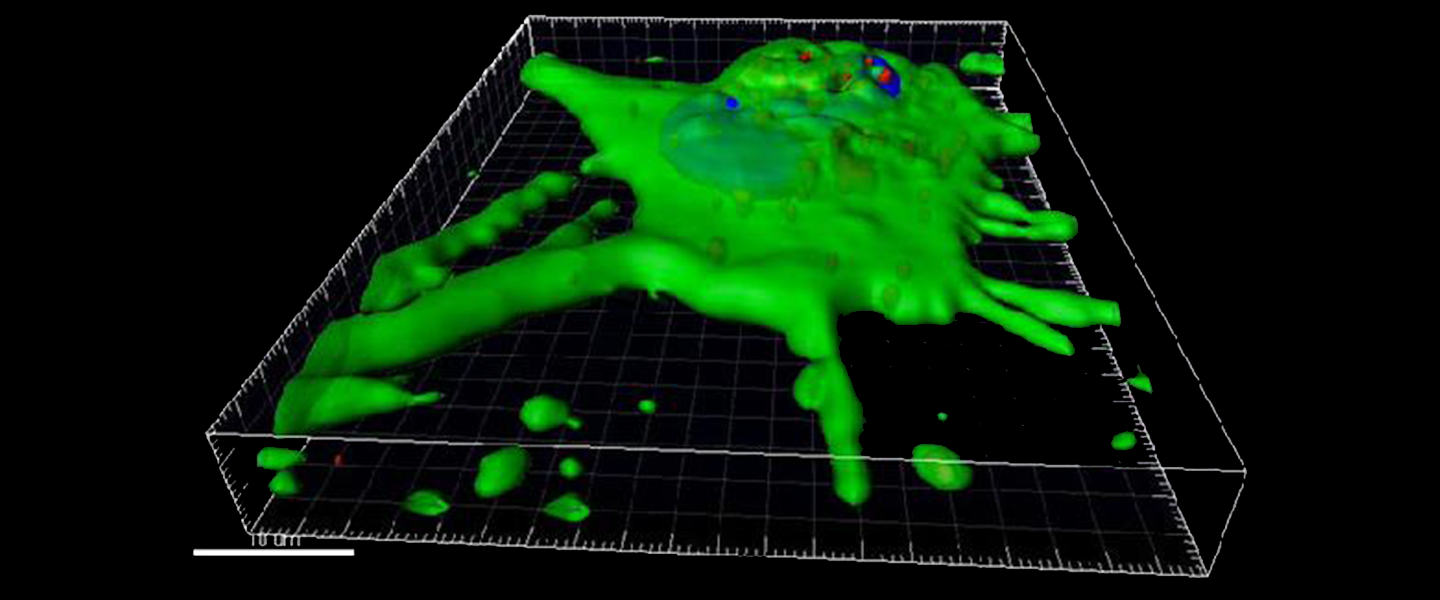
Copyright: Thum / IMTTS / MHH
Research Report 2015
Publisher:
President of the MHH
Prof. Dr. med. Christopher H. Baum
Dean of Research of the MHH
Prof. Dr. Dr. phil. Denise Hilfiker-Kleiner, PhD
Processing and contact person:
Office of the Dean of Research at Hannover Medical School
Petra Linke
Phone: 0511/ 532- 6023
Fax: 0511/ 532- 6024
E-mail: linke.petra@mh-hannover.de
Design and typesetting:
Digital Media, Hannover Medical School
Joachim Barke
Phone: 0511/ 532- 2963
Production:
Digital Media, Hannover Medical School
Telephone: 05 11/ 532- 2963
Wewould like to thank the staff of the library of the Hannover Medical School, Usage Department: Ms. Ingeborg Heering, for her support with the bibliographic information.
Wewould like to thank the staff of the Center for Information Management (ZIMt) under the direction of Mr. Dirk May for their support in the implementation of the ICT-supported data collection and the preparation of the printing process.
Alldata(including the links contained) in the research report are based on the information provided by the respective Facilities or Institutions. The entry is made without guarantee.
Themasculine form of all gender-specific descriptions applies accordingly to the feminine form.