Periodontology and peri-implantology
Treatment of diseases of the periodontium and inflammation of the tissues surrounding implants
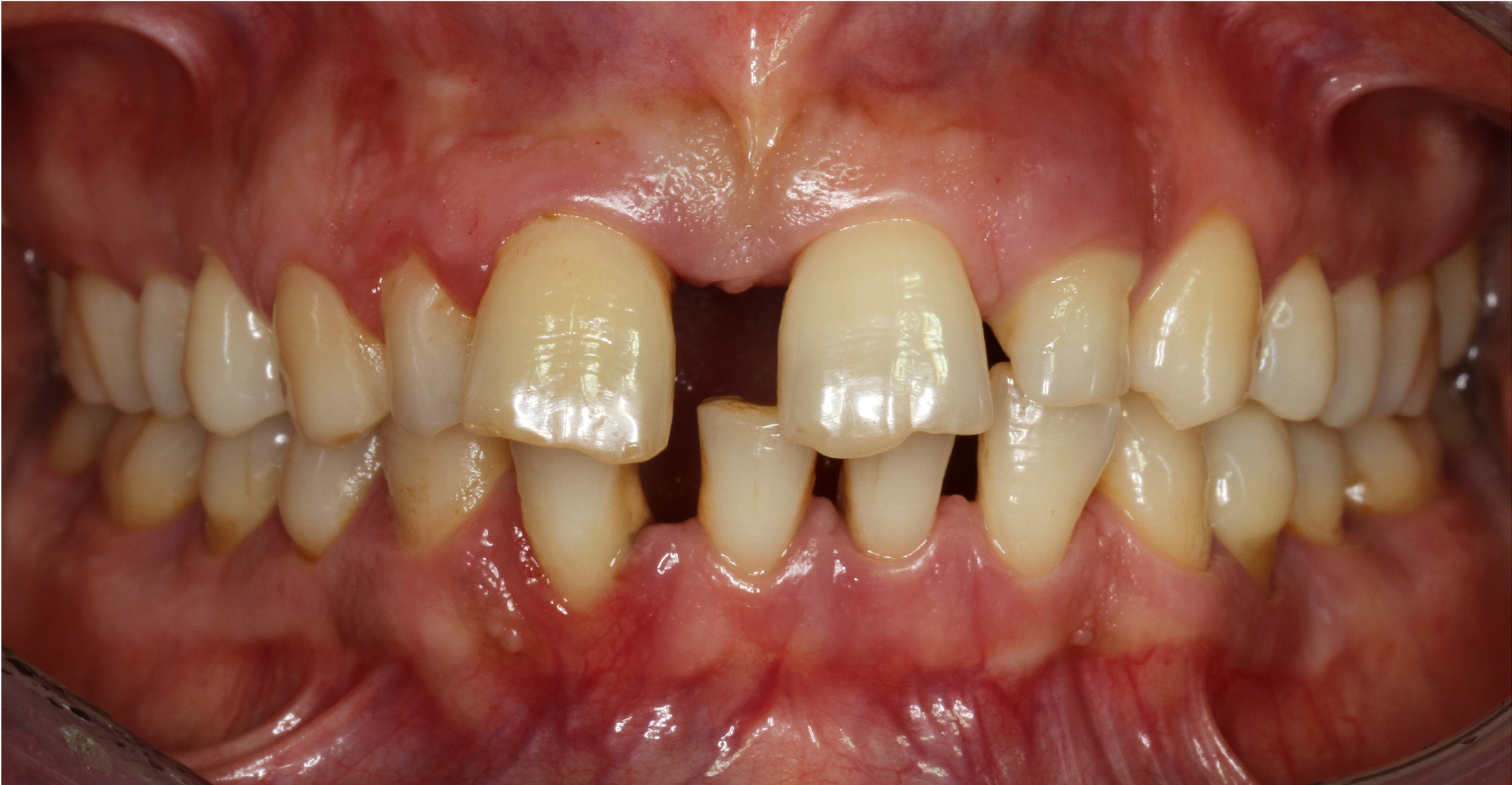
The periodontium is responsible for anchoring the teeth in the jawbone. Periodontitis is a disease of the periodontium that leads to a progressive loss of this anchorage through inflammatory tissue degradation and can lead to tooth loss if left untreated. Typical symptoms are bleeding gums, tooth loosening, tooth migration (see illustration) and bad breath. Periodontitis is caused by microbial plaque. In addition, there are a number of local and general (systemic) risk factors, such as smoking or poorly controlled blood sugar (diabetes mellitus), which can promote the development and progression of the disease. Test your individual risk of periodontitis on the official website of the German Society of Periodontology (self-test).
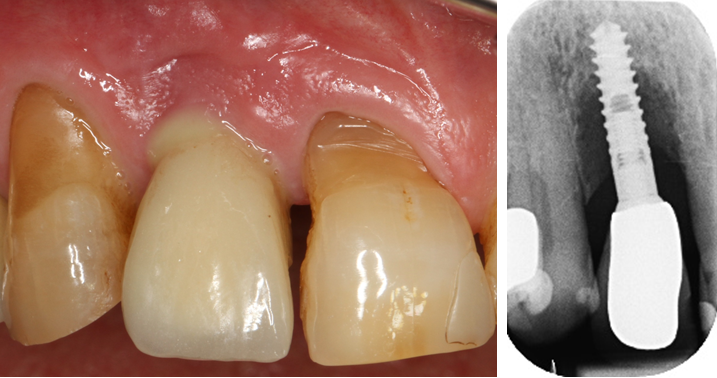
A peculiarity arises when an implant rather than the patient's own tooth is in the jaw. Dental implants usually have a screw-shaped design and are firmly fused to the jawbone (osseointegration). They can be used to replace lost teeth with fixed or removable dentures. Implants can also lead to inflammation and bone loss(peri-implantitis) in response to colonization of the implant surface with microorganisms (see illustration).
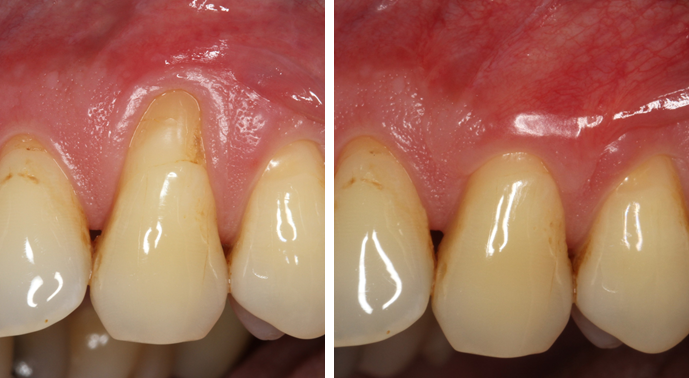
Ingingival recession, circumscribed parts of the tooth root are exposed so that the affected teeth appear longer (see illustration). In addition to this esthetic impairment, possible negative consequences include increasing hypersensitivity to thermal (hot and cold) and chemical stimuli (acidic and sweet foods) as well as an increased susceptibility to root caries, non-carious tooth substance loss, gingivitis and periodontitis. Recurrent inflammation in the gum line area (gingivitis, periodontitis) and traumatic influences (incorrect tooth brushing technique, orthodontic tooth movements, piercings in the tongue, cheek and lip area) are among the most important causes of gingival recessions.
How is ...
Successful periodontitis therapy requires your cooperation and in most cases leads to a halt in bone resorption. The earlier the periodontitis is diagnosed and the better you cooperate as a patient, the easier and more promising the therapy will be.
The treatment of periodontitis follows a systematic procedure in four sensible stages that build on each other. After comprehensive diagnostics, the first stage involves professional teeth cleaning, oral hygiene instruction, a medical consultation and therapy consultation as well as dental restoration of your teeth. The 2nd stage comprises the so-called "anti-infective therapy", in which all microbial deposits are gently and non-surgically removed from the root surface under local anesthesia. Stage 3 is optional, depending on the treatment results achieved in stage 2 and includes various surgical treatment options. In the case of suitable bone defects, it is now even possible to restore the lost periodontium (regenerative periodontal surgery). Here too, your cooperation plays a decisive role. For example, regenerative periodontal surgery is not very successful in heavy smokers and poorly controlled diabetics. The long-term goal is to restore an inflammation-free periodontium and prevent further bone loss. Lifelong periodontal aftercare is essential in order to achieve these goals and ensure the treatment results are permanent. This takes place in the 4th stage at a frequency that depends on the findings.
The general rule is: "Once a periodontitis patient, always a periodontitis patient".
The treatment of peri-implantitis is much more difficult than the treatment of periodontitis. This is partly due to the fact that the screw threads of the implants are difficult to clean. Important risk factors for the development of peri-implantitis are prosthetic restorations on the implants that are not hygienically designed, unfavorable anatomical conditions and untreated periodontitis on the remaining teeth. In many cases, treatment requires the removal of the prosthetic restoration. After non-surgical cleaning of the implant surface, a surgical procedure is necessary, particularly in the case of advanced disease, in order to gain access to the difficult-to-clean screw threads.
If you would like to have an examination or consultation at our Clinical Department, it is important that you collect very important information for us at the first consultation appointment and bring it with you. This includes the implant manufacturer, the type of fixation, in the case of cemented restorations the type of cement used, any previous bone augmentation procedures and diagnostic documents such as old x-rays, invoices and, if you have received one, your implant passport.
Gingival recessions are common and can occur in patients with or without periodontitis. Recessions in periodontitis patients are usually characterized by the fact that affected teeth are affected by gingival recession in a circular fashion, i.e. there is also a bone deficit between the teeth (see illustration). In these cases, surgical approaches to cover the exposed root surface are not promising. Conservative approaches such as regular professional dental cleanings, gentle cleaning at home and consistent fluoridation are preferable in order to prevent possible side effects such as caries, erosion, hypersensitivity and inflammatory periodontal diseases.
In selected cases - usually in patients without periodontitis - exposed root surfaces can be covered using various surgical techniques. The prerequisite is that the bone between the teeth is still completely intact and the gum recession is limited exclusively to the cheek or lip side. If you would like to make an appointment for a consultation, we would like to ask you to bring existing x-rays with you so that we can assess the bony conditions as best as possible.