Pediatric dentistry
Treatment of dental, oral and maxillofacial diseases in children and adolescents
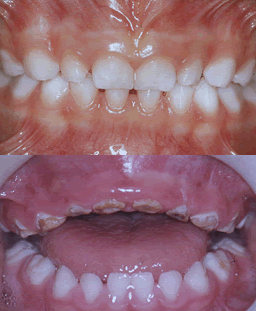
Milk teeth are more susceptible to decay than permanent teeth. The thinner hard dental tissue is also less mineralized. This leads to a more rapid spread of caries, which can reach the tooth nerve. Severe pain occurs and the preservation of the tooth is at risk. Premature loss of milk teeth impairs chewing and, under certain circumstances, aesthetics and speech development. The change of teeth and growth of the facial skull can be impaired and result in lengthy orthodontic or speech therapy treatment.
Regular visits to the dentist are therefore recommended from a very early age, during the period in which the first milk teeth appear in the mouth. This usually happens in the 6th to 7th month of life. Further check-ups are recommended between the ages of 10-20 months and 21-29 months. Here, the mouth and teeth are examined, tips on dental care and nutrition are given and initial contact is made between the dental team and the young patient. Between the 34th month of life and the 6th birthday, a further 3 dental examinations are recommended.
These serve to assess the risk of caries, provide nutritional and oral hygiene advice with the aim of reducing the risk of caries in the child by reducing the consumption of sugary foods and drinks and improving oral hygiene, recommending suitable fluoridation agents to increase the enamel's resistance to caries (toothpaste, varnishes, fluoridated table salt, etc.). If caries is already present, it should be treated as early as possible. The smaller the caries and the older the child, the better the treatment will work. If pain has already occurred or there have already been numerous unsuccessful treatment attempts by other dentists, treatment is often more difficult.
First and foremost, we try to take time for your child. This procedure may take several treatment appointments. This is the only way to overcome fears and build trust, which often makes conventional treatment possible from the age of around three. The treatment itself is carried out using the same methods and materials as for adults.
Questions & Answers from the Pediatric Dentistry & Prophylaxis Working Group
As soon as the first milk teeth are present, regular visits are advisable. The yellow child examination booklet provides for three early dental check-ups:
- around the 6th-7th month of life (parallel to the pediatric U5), as this is when the first incisors usually erupt into the oral cavity,
- between the 10th and 20th month of life (between the U6 and U7) and
- the 21st-29th month of life (with or after the U7), as the milk teeth are now usually fully present.
This is when the mouth and teeth are examined, tips on dental care and nutrition are given and initial contact is made between the dental team and the young patient.
A further three dental examinations are recommended between the age of 34 months and the 6th birthday. These serve to assess the risk of caries, provide nutritional and oral hygiene advice with the aim of reducing the number of germs in the child by reducing the consumption of sugary foods and drinks and improving oral hygiene, recommend suitable fluoridation agents for enamel hardening (fluoridated table salt, toothpaste, etc.) and, if necessary, prescribe fluoride tablets. If caries is already present, it should be treated as early as possible.
Milk teeth are more susceptible to caries, as the already thinner tooth structure is less mineralized. This leads to a more rapid spread of caries to the nerve of the tooth, causing inflammation and severe pain and jeopardizing the preservation of the tooth. If the inflammation spreads further, it can also affect the general health of children.
Milk teeth are important! Premature loss of milk teeth can lead to several problems:
- Impairment of aesthetics and speech development
- Impairment of chewing function
- Disorders during tooth change due to missing space maintainer function
- Disorders in the development of the facial skull
This may necessitate lengthy orthodontic or speech therapy treatment.