Elective course I: Anatomy Meets Anesthesia
Module code: MSE_WP_247
In anesthesia, numerous procedures require specific and detailed anatomical knowledge. In this elective course, you will gain an insight into anesthesiological work and learn how anatomical and anesthesiological knowledge are interlinked to contribute to safe and professional anesthesiological care. Using an interactive case study, you will have the opportunity to deepen your anatomical knowledge on the specimen. You will learn the basics of airway management, chest tube placement, CVC placement, tracheotomy, emergency sonography (eFAST) and regional anesthesia using anatomical specimens and practice phantoms. In the dissection room and anaesthesia simulation center, you will have the opportunity to immerse yourself in anatomy and anaesthesia and also get to know the anaesthesiology intensive care unit.
Elective course II: Safety in difficult situations (HAINS week)
Module code:MSE_WP_541
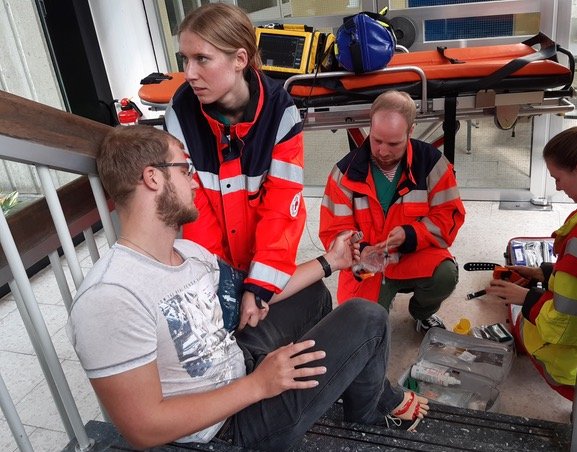

In this course, previously taught content of general clinical anesthesia is repeated and deepened. This includes preoperative patient evaluation, knowledge of induction, administration and withdrawal of general anesthesia, as well as indications and contraindications and the administration of regional anesthesia. Furthermore, specific content of the individual surgical disciplines is developed using case studies.
Special emphasis is placed on dealing with emergency situations and unexpected events and complications. The anaesthesia simulator (HAINS), which is already familiar from the compulsory course, is used for this purpose. In addition, there will be daily observations in the operating theaters. Another part of the course is the delivery of bad news. This is practiced with simulated patients. Where possible, students are trained to perform a coniotomy and chest tube placement in forensic medicine.
Anaesthetists often have to make quick and precise decisions in their day-to-day work. Routine work only appears calm when anesthesia, intensive care or emergency treatment is carried out with sustained attention. The profession of anaesthetist requires comprehensive knowledge of physiology and pharmacology as well as manual dexterity.
The ability to work with foresight and team spirit is particularly important in critical situations and incidents. Simulation is a recognized training tool in anaesthesia to get to know critical situations in a protected atmosphere and to reflect on one's own behaviour. Other topics include dealing with critically ill patients and communication tasks such as breaking bad news.
Elective course II: Pediatric Advanced Life Support (PALS)
Module code: MSE_WP_573
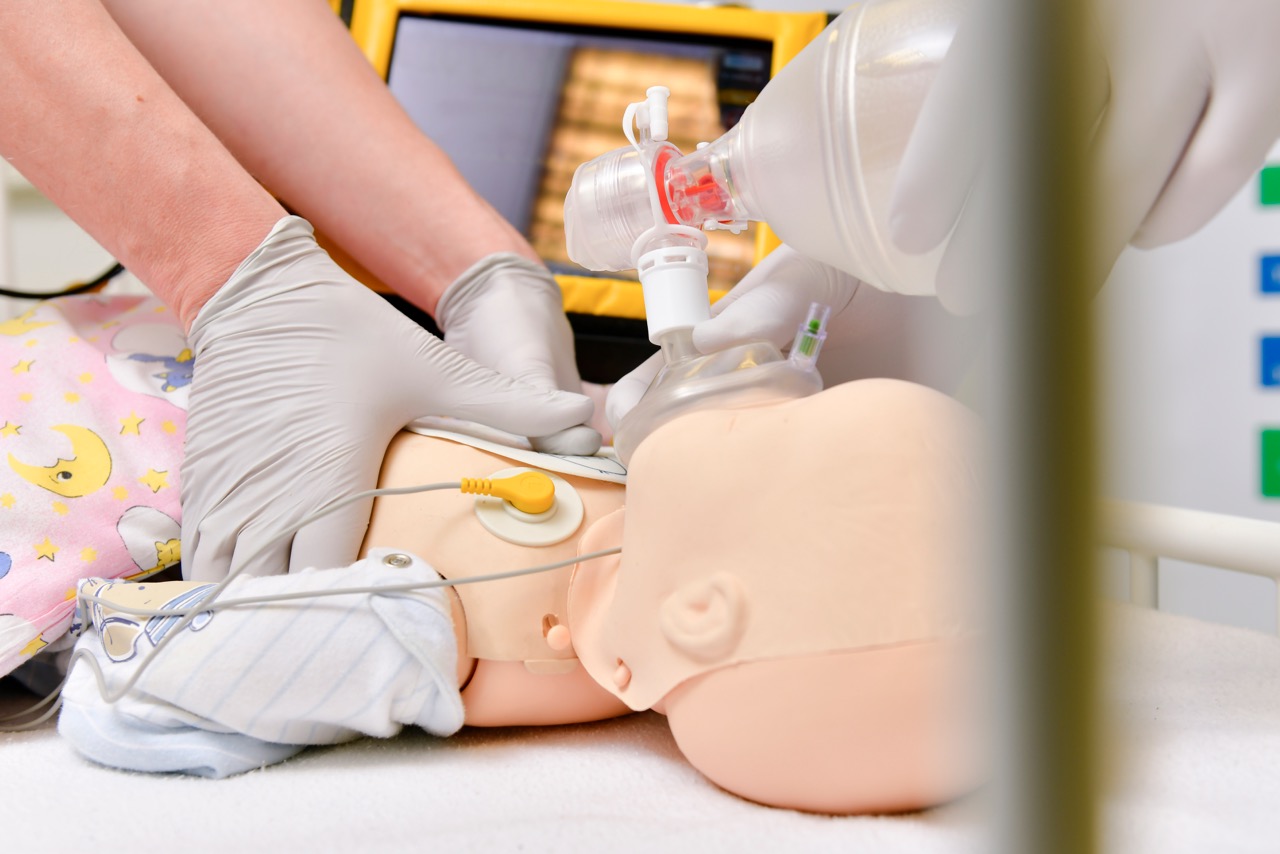
The focus is on learning techniques for treating critically ill children and infants. The emphasis is on the rapid algorithm-based recognition of respiratory and cardiac disorders. Learning and applying a symptom-oriented therapy algorithm to stabilize critically ill children and infants.
A particular focus is on training effective teamwork and team resource management (TRM). Further focal points are: The management of respiratory and cardiovascular emergencies in children in theory and practice (case simulation on the full-scale child simulator with subsequent debriefing). Techniques for securing the airway, setting up vascular accesses (intravenous/intravenous) and electrotherapy for cardiac arrhythmias.
As part of the elective subject, it is possible to obtain an internationally valid certificate ("Pediatric Advanced Life Support Provider") from the American Heart Association after passing the written and practical examination. The costs of the certificate are covered by LOM teaching funds from the Clinical Department of Anaesthesiology and Intensive Care Medicine.
Elective course II: Obstetric and anesthesiological emergencies in an interdisciplinary team
Module code: MSE_WP_584
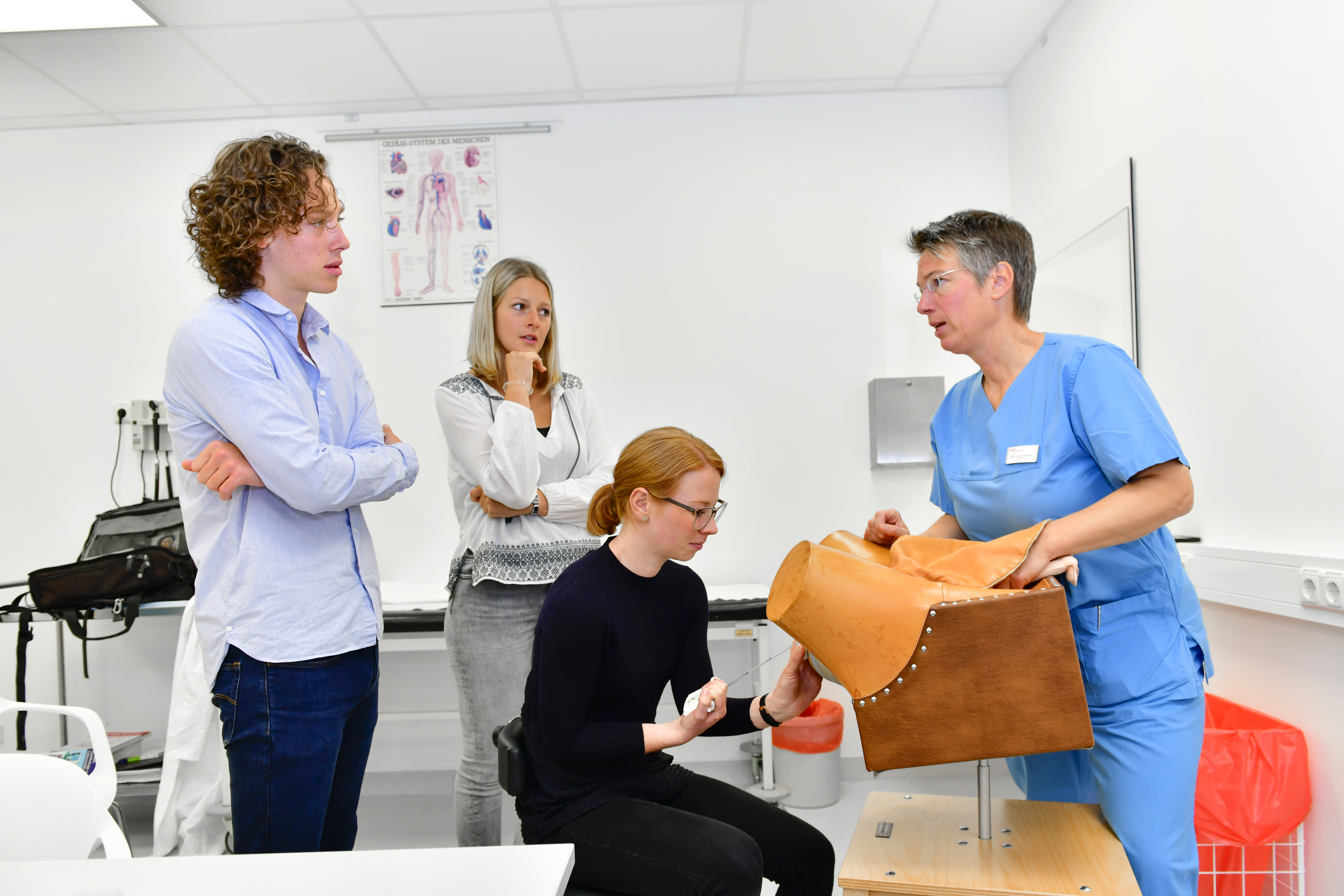
The focus is on learning techniques for recognizing and treating critically ill mothers and newborns in the birth situation from the perspective of gynaecology and anaesthesia. Interdisciplinary and interprofessional collaboration in a high-risk environment such as obstetrics is characterized by many challenges. A wide variety of incidents with potential implications for mother, child and the entire treatment team must be managed as a team. Insights into the fields of activity of obstetrics, anesthesia and pediatrics will highlight the various treatment concepts and their interaction.
Further course contents are :
- Mechanics of birth / techniques of spontaneous delivery
- Indications and procedure of a caesarean section
- Analgesia in obstetrics
- Emergency caesarean section from different perspectives
- CTG training
- Episiotomy training
- Birth on the trainer
- ppH - Critical bleeding during childbirth
- Spinal anesthesia in theory and practice on the simulator
- Central venipuncture and intraosseous puncture in theory and practice on the simulator
- Simulation of common obstetric incidents
- Simulation of an emergency caesarean section
- Neonatal care - resuscitation
- Training in effective teamwork and Crisis Resource Management (CRM)
Registration takes place via your FACT web service.
Elective course II: Diving medicine
Module code: MSE_WP_604
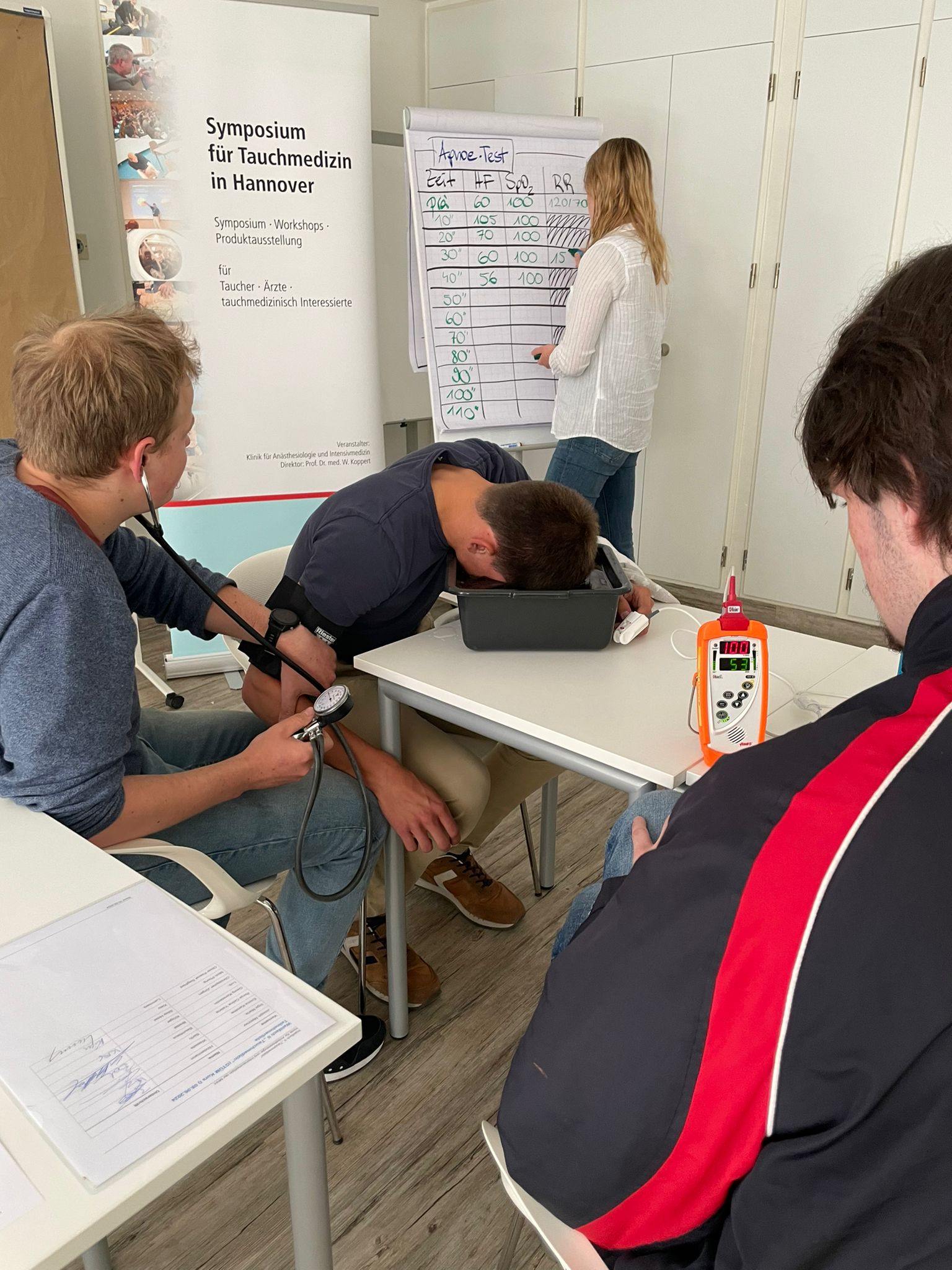
Learning objectives and content
- physical and (patho-)physiological basics of diving medicine in relation to the necessity of a diving fitness examination.
- Independent performance of a diving fitness examination (TTU) according to GTÜM specifications
- Tympanoscopy to assess the eardrum as part of the TTU
- Fitness to dive in the context of previous illnesses and long-term medication
- Indications and termination criteria for exercise ergometry in the context of a TTU
- Resuscitation with the aid of an automatic external defibrillator and extraglottic airway support in the context of an incident during exercise ergometry
- Hyperbaric physics
- Diving-related physiology
- Recreational diving, apnea diving. Dive tables, dive computers
- Resuscitation training
- Acute dysbaric diseases
- Oxygen intoxication, inert gas effects
- Hyperbaric pathophysiology (decompression and apnea)
- Chronic dysfunctional diseases
- Regulations for diving work
- Diving fitness assessment for children
- Medication under pressure
- Contraindications Pressure-independent pathologies
- Diving accidents, diving incidents
Successful completion of the elective course in diving medicine enables certification for "Diploma I, Diving Fitness Examinations" by the GTÜM (Society for Diving and Hyperbaric Medicine) within two years of completing the elective course (and fulfilling the other requirements of the GTÜM) upon application for licensure as a physician.