Neuropsychiatric diseases
As an animal model for neuropsychiatric diseases we use, among other things, prepulse inhibition (PPI) of the acoustically induced startle response. This is a measure of an automatic mechanism of response suppression in the brain ("sensorimotor gating"), which is reduced in some neuropsychiatric disorders, such as schizophrenia and Tourette's syndrome. Animal experimentally induced PPI deficits are therefore considered valid models to study these disorders. In particular, we are investigating the effects of DBS on pharmacologically induced PPI deficits as well as on other cognitive and emotional disorders associated with these deficits. We have already shown that the neuronal activity of pharmacologically treated rats resembles that of patients with Tourette's, and that DBS of clinically relevant brain regions improves both PPI deficits and neuronal changes. Here, too, we use the information obtained to further develop adaptive stimulation strategies.
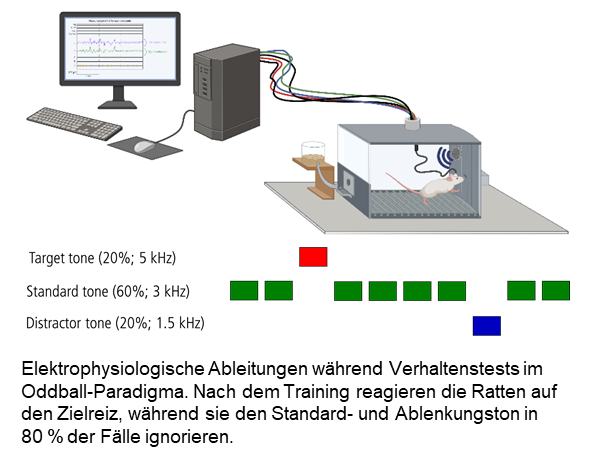
Another approach deals with the neuronal processing of relevant and irrelevant environmental information. This is also disturbed in certain neuropsychiatric disorders such as schizophrenia. As a behavioral paradigm, we use the so-called three-class oddball paradigm, in which the rat must ignore a frequent standard tone and a rare distractor tone, but must react to a rare target tone with a behavioral response. During the behavioral paradigm, the rats' neural activity is recorded via previously implanted electrodes and, among other things, the effect of certain neuropharmaceuticals on the neural processing of relevant and irrelevant information is investigated.
Decker FM, Jelinek J, Korb K, Fogaing Kamgaing F, Alam M, Krauss JK, Hermann EJ, Schwabe K. Neural processing of auditory stimuli in rats: Translational aspects using auditory oddball paradigms. Behav Brain Res. 2025 Mar 28;482:115428. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbr.2025.115428
Abdulbaki A, Doll T, Helgers S, Heissler HE, Voges J, Krauss JK, Schwabe K, Alam M. Subthalamic Nucleus Deep Brain Stimulation Restores Motor and Sensorimotor Cortical Neuronal Oscillatory Activity in the Free-Moving 6-Hydroxydopamine Lesion Rat Parkinson Model. Neuromodulation. 2023 Mar 29:S1094-7159(23)00023-5. DOI: 10.1016/j.neurom.2023.01.014
Abdul Nabi Ali A, Alam M, Klein SC, Behmann N, Krauss JK, Doll T, Blume H, Schwabe K. Predictive accuracy of CNN for cortical oscillatory activity in an acute rat model of parkinsonism. Neural Netw. 2022 Feb;146:334-340. DOI: 10.1016/j.neunet.2021.11.025
Elle T, Alam M, Voigt C, Krauss JK, John N, Schwabe K. Deep brain stimulation of the thalamic centromedian-parafascicular nucleus improves behavioral and neuronal traits in a rat model of Tourette. Behav Brain Res. 2020 Jan 27;378:112251. DOI: 10.1016/j.bbr.2019.112251
Schwabe K, Krauss JK. What rodent models of deep brain stimulation can teach us about the neural circuit regulation of prepulse inhibition in neuropsychiatric disorders. Schizophr Res. 2018 Aug;198:45-51. DOI: 10.1016/j.schres.2017.06.033
Rumpel R, Alam M, Schwarz LM, Ratzka A, Jin X, Krauss JK, Grothe C, Schwabe K. Neuronal firing activity in the basal ganglia after striatal transplantation of dopamine neurons in hemiparkinsonian rats. Neuroscience. 2017 Sep 30;360:197-209. DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2017.07.069
Alam M, Rumpel R, Jin X, von Wrangel C, Tschirner SK, Krauss JK, Grothe C, Ratzka A, Schwabe K. Altered somatosensory cortex neuronal activity in a rat model of Parkinson's disease and levodopa-induced dyskinesias. Exp Neurol. 2017 Aug;294:19-31. DOI: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2017.04.011
Jin X, Schwabe K, Krauss JK, Alam M. Coherence of neuronal firing of the entopeduncular nucleus with motor cortex oscillatory activity in the 6-OHDA rat model of Parkinson's disease with levodopa-induced dyskinesias. Exp Brain Res. 2016 Apr;234(4):1105-18. DOI: 10.1007/s00221-015-4532-1
Angelov SD, Dietrich C, Krauss JK, Schwabe K. Effect of deep brain stimulation in rats selectively bred for reduced prepulse inhibition. Brain Stimul. 2014 Jul-Aug;7(4):595-602. DOI: 10.1016/j.brs.2014.03.013
Alam M, Capelle HH, Schwabe K, Krauss JK. Effect of deep brain stimulation on levodopa-induced dyskinesias and striatal oscillatory local field potentials in a rat model of Parkinson's disease. Brain Stimul. 2014 Jan-Feb;7(1):13-20. DOI: 10.1016/j.brs.2013.09.001
Collaborations
Prof. Dr. Holger Blume (Institute of Microelectronics, LUH)
Prof. Dr. Helge Frieling, Dr. Mathias Rhein (Clinical Department of Psychiatry, Social- and Psychological Therapy, MHH)
Funding
DFG Research Unit 2591 - SCHW1176/7-2