Computed tomography (CT)
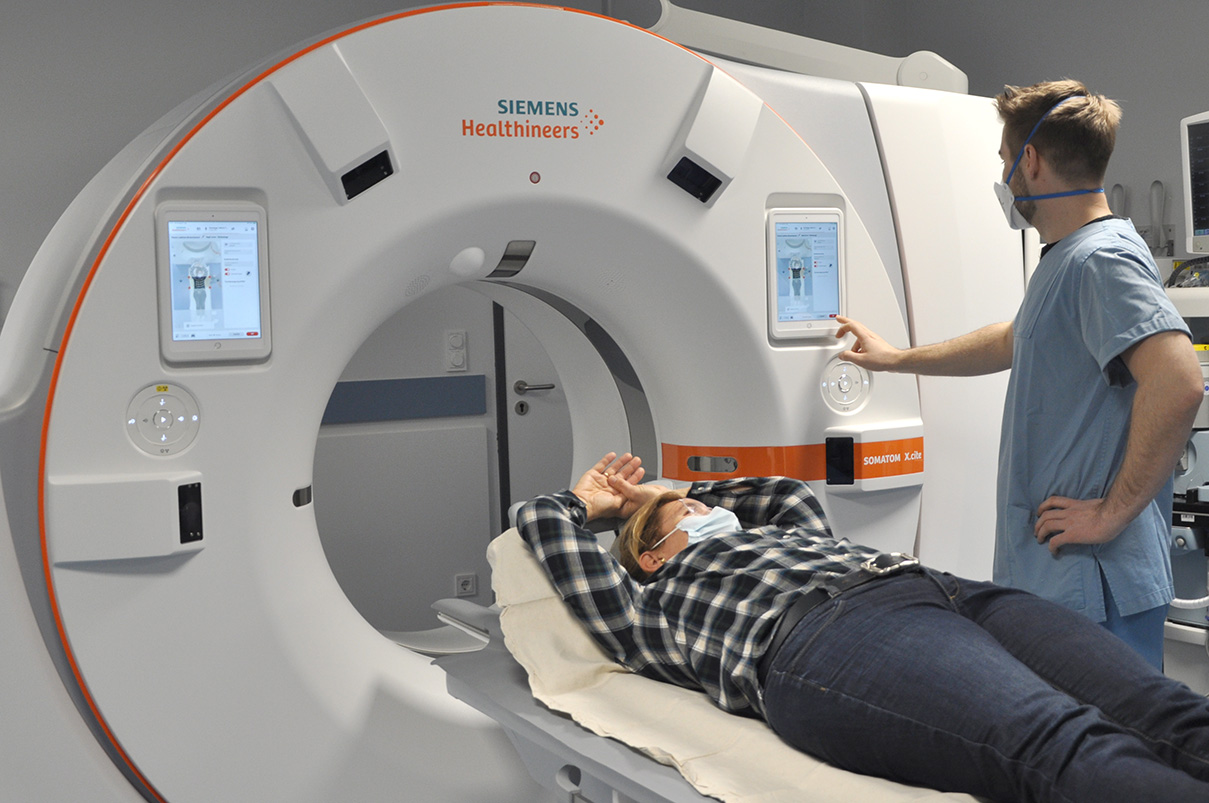
Computed tomography is an X-ray examination that allows a detailed view of the inside of the human body. By recording a volume data set, examined body regions can be viewed in detail from any direction and thus displayed without superimposition.
Our devices are used to diagnose the entire body. Special emphasis is placed on the examination of the chest, abdominal organs (liver, kidneys, pancreas) and the various vascular systems of the body (pulmonary vessels, coronary arteries, renal arteries, aorta, iliac vessels). see abdominal radiology
We also carry out CT-supported interventions. These include diagnostic punctures to obtain tissue, insertion of drains into abscesses or other fluid collections, as well as local therapy procedures such as radiofrequency or microwave ablation to treat tumorous lesions of the liver or kidney, for example.
Newer examination techniques include, for example, imaging of the heart (coronary vessel imaging).