What is orthoptics?
A rare profession introduces itself:

The orthoptist deals with the prevention, detection (diagnostics) and treatment (therapy) of
- strabismus
- visual impairments
- Disorders of monocular and binocular vision
- eye tremors
- Eye movement disorders
Patients often come to us with the following complaints:
- Strabismus
- double vision
- Eye muscle paralysis
- Reduced vision on one or both sides
- Eye-related head misalignment
- eye tremor, headaches
- reading disorders
The aim of orthoptics is to prevent and improve visual and strabismus disorders and their permanent damage. By restoring or maintaining monocular and binocular vision, orthoptics counteracts visual and perceptual deficits in daily life, resulting in better integration and a higher quality of life.
Link for further information from our professional association: https://orthoptik.de/
An orthoptic examination
This examination covers many areas of vision.
Binocular vision is often tested at the beginning using the Bagolini tail test. This tests the coarsest aspect of binocular vision, i.e. the cooperation of both eyes.
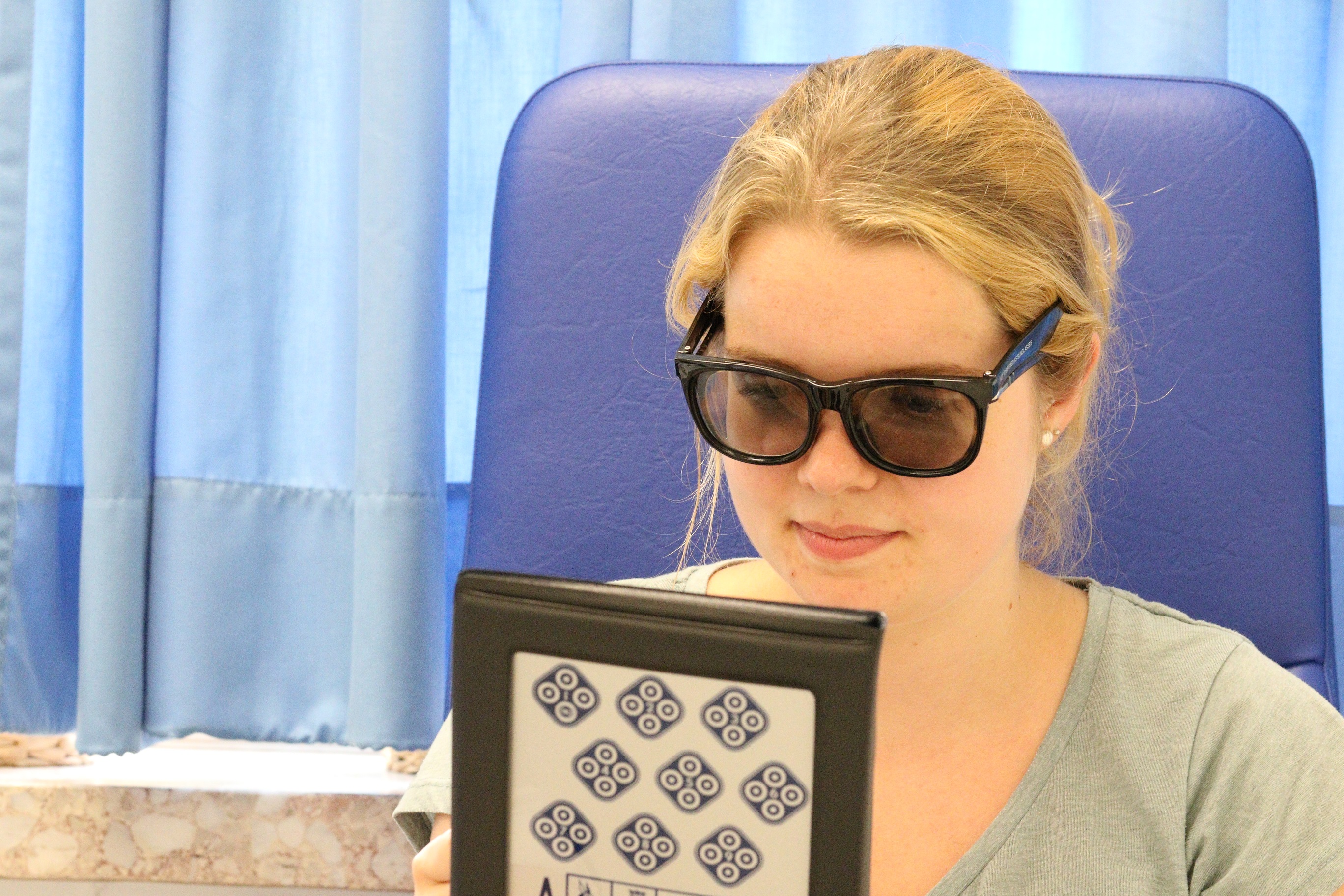
Next, stereo vision (a finer level of binocular vision, colloquially known as 3D vision) is tested. This can be tested using the Lang test and/or Titmus test, for example. The photo shows an examination with the Titmus test.
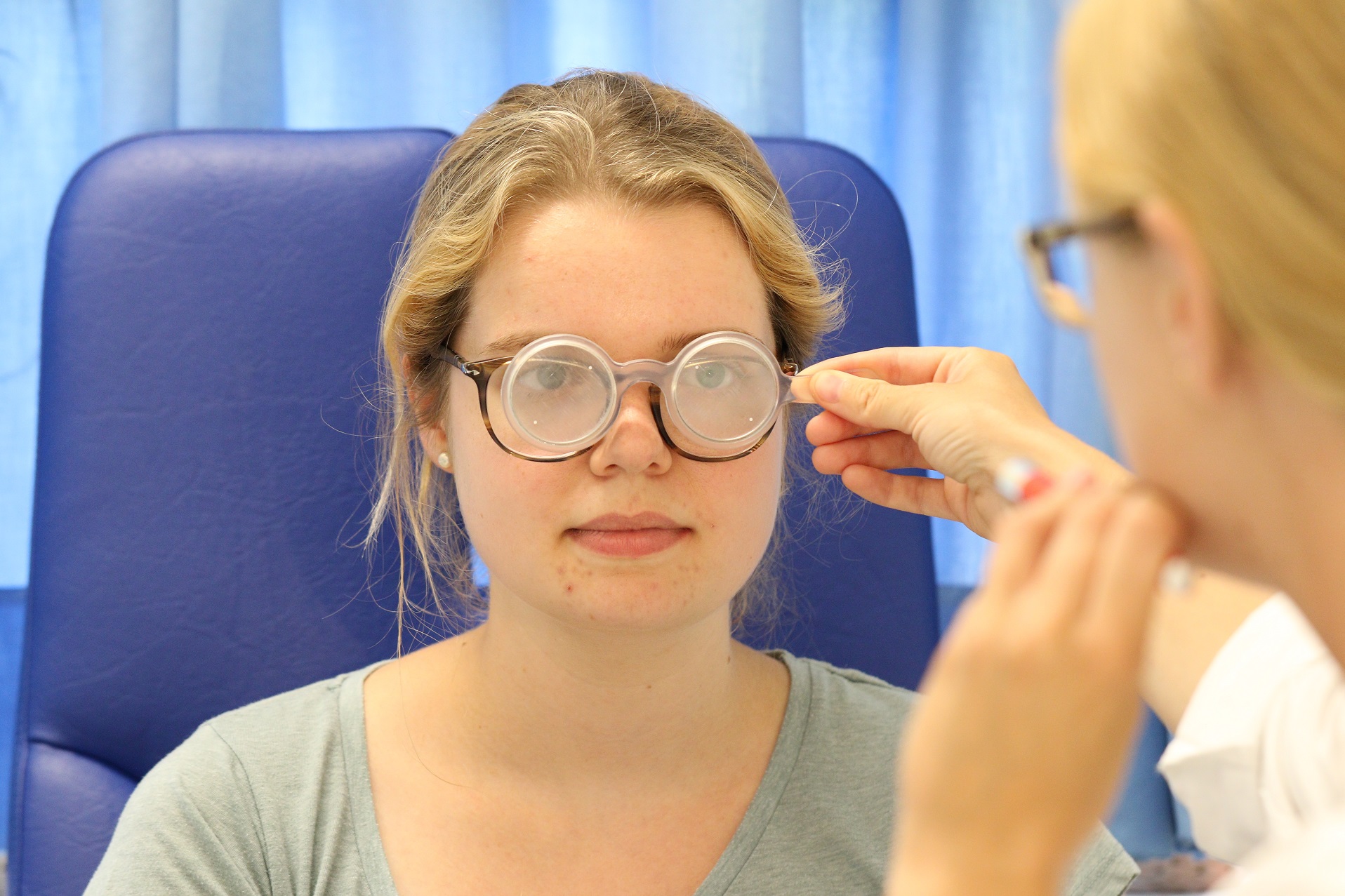
The photo on the right shows an alternating prism cover test to assess the position of the eye and measure the squint angle. One eye is covered with a cover. If there is a misalignment, this is measured using prisms. To do this, the cover is held alternately in front of the right and left eye and the prism is held in front of the squinting eye. This is how the squint angle is measured.
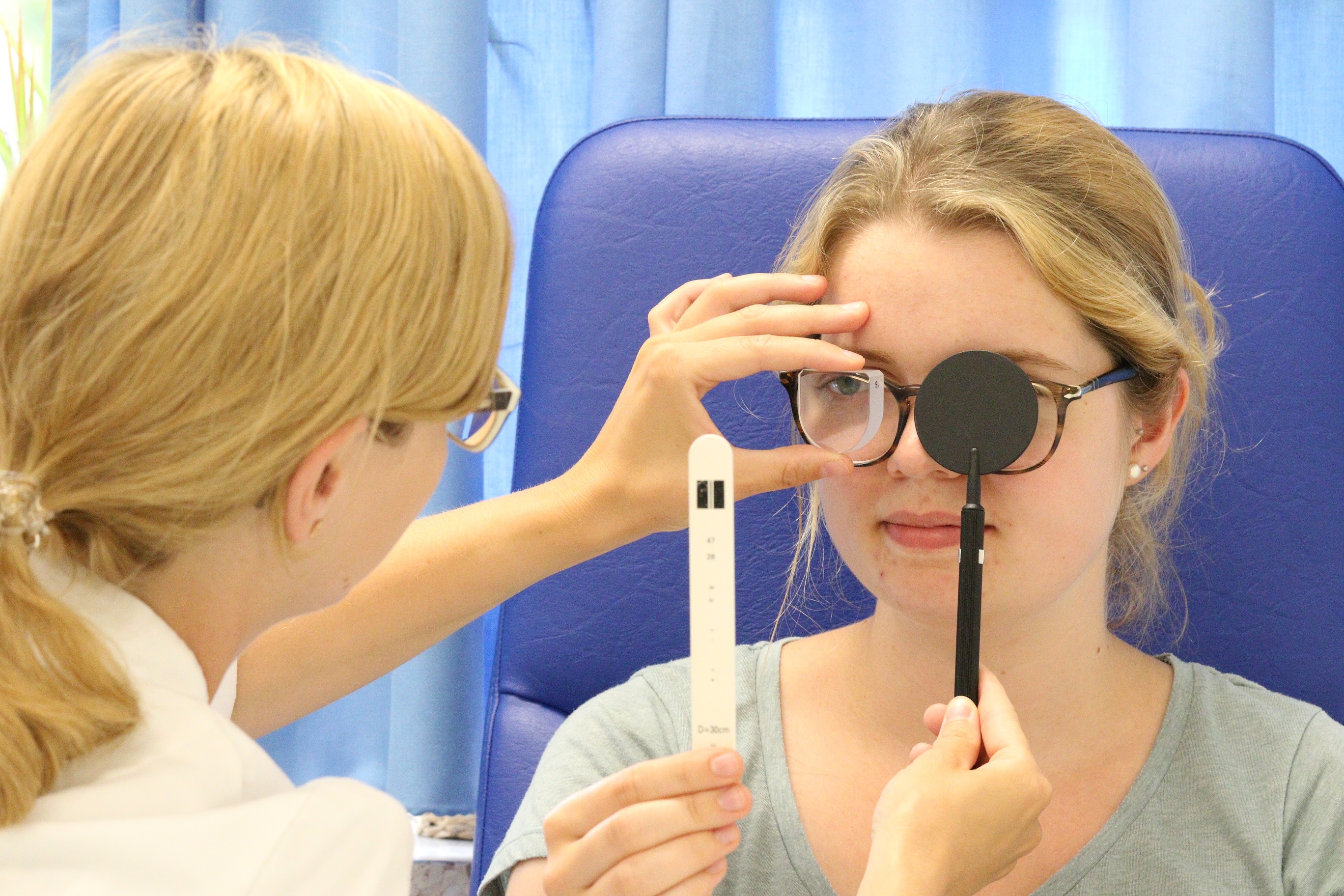
The motility of the eyes is also checked.
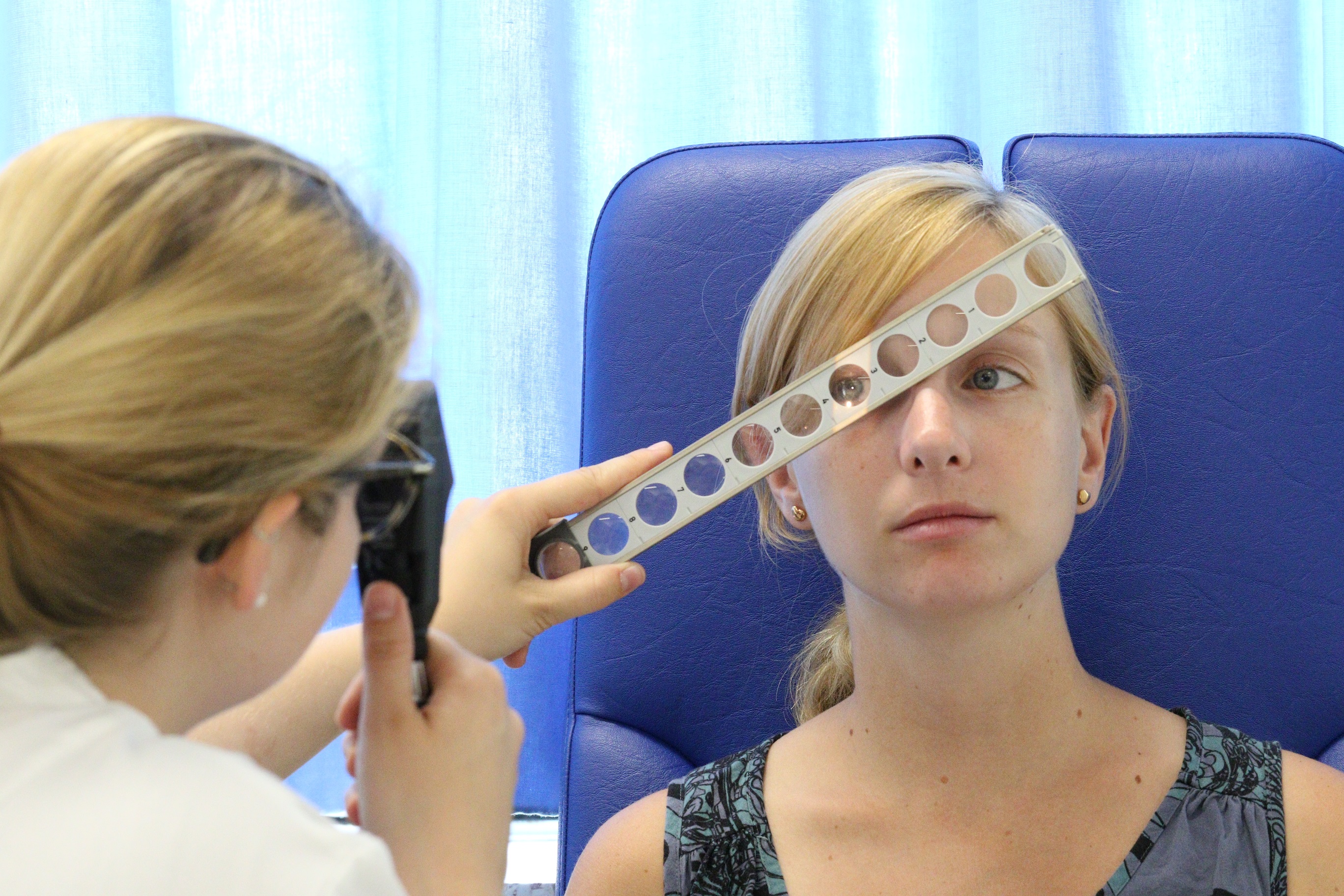
In many cases, especially in children, a skiascopy is also carried out. Before the examination, the pupil is dilated with eye drops and then the refraction (= spectacle values) is measured with a wide pupil. See photo on the right.
Many other examinations are selected according to the patient's judgment, clinical picture and cooperation. Age-appropriate examinations are carried out on children. An "eye test", which gives an indication of visual acuity, can be carried out on the youngest children from the age of 3 months.
For adults, other examinations can be carried out or evaluated in a different setting than for children.