Alcohol Action Week 2024
June 08-16
Many people in Germany drink too much alcohol. Often without being aware of the health risks. Alcohol consumption is one of the causes of over 200 diseases. Nevertheless, beer, wine & co. are part of everyday life for most people in Germany.
This is why the Alcohol Action Week, under the motto "Alcohol? Less is better!" is encouraging people to rethink their personal and social approach to the "number one drug of the people".
Alcohol? Less is better!
Alcohol Action Week - Alcohol? Less is better!
German Center for Addiction Issues e.V.
Addiction in the workplace
Occupational safety
Occupational safety can be acutely endangered by various factors, for example by the influence of a psychoactive substance. In this respect, the consumption of alcohol and drugs, as well as certain medications in the workplace, poses a risk to users and third parties. There are clear legal rules that must be observed. Depending on whether an acute risk is clearly related to substance use, a clarification discussion must be initiated during the intervention or the step-by-step plan is applied.
The influence of alcohol, drugs and other intoxicating substances causes a reduction in the ability to work. This also explicitly includes medication that has a psychoactive effect. In this context, working under the influence of these substances is considered an occupational risk.
If there are indications that an employee is under the acute influence of a psychoactive substance, it is the responsibility of the supervisor to immediately check whether the person concerned can still carry out the work without endangering others.
Occupational safety can also be acutely endangered by behavioral restrictions, such as lack of concentration due to problematic media use. These abnormalities also require intervention by the executive responsible.
Accident prevention regulations based on the seventh German Social Code (SGBVII) apply to prevent accidents. In accordance with Section 15 SGB VII, the employers' liability insurance associations, as the statutory accident insurance institutions, issue regulations for safety and health at work(DGUV Regulation 1).
According to the accident prevention regulation "Principles of Prevention", employers are obliged under § 7 to ensure that work tasks are not assigned to persons who are clearly incapable of carrying them out without endangering themselves or others.
DGUV Regulation 1 Principles of prevention. Accident prevention regulation
§ 7 Qualification for activities
(2) The employer must not employ insured persons who are clearly unable to carry out work without endangering themselves or others.
§ Section 15 General support obligations and conduct
(2) Insured persons must not use alcohol, drugs or other intoxicating substances to put themselves in a state that could endanger themselves or others.
(3) Paragraph 2 also applies to the use of medication.
The company physician may be consulted if it is necessary to determine suitability for the job. It is advisable to consult a company physician, especially in the case of abnormalities that cannot be clearly attributed to alcohol and could play a role in connection with other mental or physical limitations.
For their part, employees are also obliged to ensure that their behavior does not put themselves or others at risk. Section 15 SGB VII stipulates that they must not put themselves in a state that could endanger themselves or others by consuming alcohol, drugs or other intoxicating substances (also applies to medication).
If an acute risk to occupational safety due to substance use is identified, it is in the interests of addiction prevention and addiction help in the workplace for the supervisor to initiate an intervention. The risk is taken as an opportunity for a clarification discussion. If the connection to substance use is obvious, a discussion at the first stage of the step-by-step plan must be initiated.
Alcohol poisons body cells. Always.
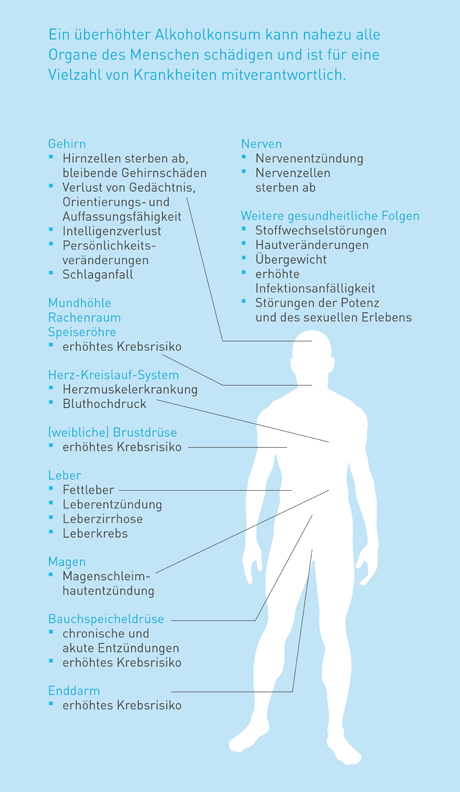
Every glass too many can be harmful to your health. This excess is quickly reached. And it is a mistake to believe that only alcohol dependence leads to serious damage to health. Alcohol consumption is always risky. That is why people should drink as little alcohol as possible or none at all.
In Germany, many people die every year as a result of alcohol consumption or the combined consumption of alcohol and tobacco.
The few publications available on alcohol-related deaths in Germany show a high probability of underestimation. This is because only those deaths that can be 100% attributed to alcohol consumption are usually recorded. These are, for example, diagnoses such as alcohol dependence syndrome or alcoholic liver disease.
Studies show that more than 200 diseases are partly caused by alcohol consumption. The diagnoses that are solely attributable to alcohol consumption therefore only make up a minority of the annual alcohol-related deaths. In fact, the number of people who die from or with alcohol consumption is higher. For Germany, a WHO calculation in 2016 identified around 19,000 women and 43,000 men among the deaths that can be attributed solely to alcohol.
Source: Health - Alcohol Action Week 2024 (aktionswoche-alkohol.de)
Alcohol is primarily broken down by the liver. Excessive alcohol consumption is therefore particularly damaging to the liver. As the female liver breaks down alcohol more slowly for hormonal reasons, the damage usually occurs earlier in women: Fatty liver, liver inflammation, liver cirrhosis and even liver cancer.
High alcohol consumption can also lead to acute and permanent inflammation of the pancreas. The risk of cancer also increases.
Chronic alcohol consumption often leads to cardiac arrhythmia, myocarditis and high blood pressure. Alcohol consumers are twice as likely as non-drinkers to suffer from high blood pressure, which resists all medical treatment. This significantly increases their risk of suffering a stroke.
Alcohol attacks cells in the mouth and throat even while you are drinking alcohol. Regular and excessive consumption increases the risk of cancer. It increases significantly if you also smoke.
Even two small glasses of beer or wine a day increase the risk of breast cancer. Regular high consumption increases it by a factor of 1.5.
Long-term alcohol consumption increases the risk of developing bowel cancer. People with a medical or family history of chronic inflammatory bowel disease should avoid alcohol.
Alcohol causes nausea and vomiting. Drinking too much alcohol on a regular basis can inflame the stomach lining. Consuming more than 30 - 40 grams of alcohol per day often leads to injuries to the stomach lining or - as a result of vomiting - to stomach bleeding. The mucous membrane of the small intestine is also often damaged. As a result, it can no longer absorb important nutrients such as vitamins or minerals. This results in deficiency symptoms.
Too much alcohol severely disrupts the production of sex hormones. In men, this often leads to impotence. The testicles shrink, the semen is damaged and the mammary glands enlarge.
Alcohol is high in calories. The beer belly also grows with wine, schnapps and cocktails.
Offers of support
internal
Addiction counseling of the MHH Addiction Outpatient Clinic of the MHH (ABAM)The professional addiction outpatient clinic of the MHH
Other internal advice centers for MHH employeesexternal
Addiction and drug counseling centers in the Hannover region Alcohol? Know your limit - a BZgA campaignInformation and tips on health-conscious alcohol consumption
Outpatient clinic for addiction disorders at the Wahrendorff Clinic