Prevention and rehabilitation
Head of the research unit
Deputy Head
Office
Research associates
Anna Brager
Dr. Iris Brandes
Katharina Bremer
Ricarda Brender
Lea Decker
Dr. Andrea Dehn-Hindenberg
PD Dr. Maren Dreier
Dr. Dr. Vitali Gorenoi
Silke Kramer
Bettina Kruckenberg
Marie-Christin Lenz
Olivia Nentwig
Sibel Ünlü-Reske
Isabell von Holt
Assistants
Rebecca Brandner
Shirin Othmer
Seyma-Nur Toklu
The research focus on prevention and rehabilitation also examines epidemiological issues.
Until summer 2013, the area of palliative and ageing research was part of this research area. Current projects and publications can be found on the website of the Institute of General Medicine and Palliative Medicine at the MHH.
The endowed chair "Prevention and Rehabilitation in Systems and Health Care Research" was established in July 2004 to strengthen prevention and rehabilitation in Germany at the Institute of Epidemiology, Social Medicine and Health Public Research and ended in 2010.
The endowed chair focused on research and qualification (teaching) as well as regional and nationwide structural development and strengthening the relevance of prevention and rehabilitation in the public perception.
Current projects
#FREI DAY FOR FUTURE - Evaluation of the impact of the FREI DAY (Whole School Approach) learning format on healthy and ecologically sustainable lifestyles and living conditions in schools and communities CTC - Effects of Communities That Care on the development of community prevention structures and the local introduction of evidence-based prevention measures BREAKOUT - Rehab for young adults with obesity EVA-Weitblick - Evaluation of the implementation and effectiveness of the framework strategy for school health promotion Weitblick BeBePrä - Strengthening the focus on needs and requirements in prevention CTC-EFF - Effectiveness of the Communities That Care community prevention system Green List Prevention - Evidence Register Sigmoidoscopy as an evidence-based screening method for colorectal cancer - a possible option? (SIGMO)
Completed projects
Funding body
BMBF
Sub-project at the MHH
Prof. Dr. Ulla Walter (project management)
Dr. Dominik Röding (project coordination)
Sub-project at the LUH
Prof. Dr. Christiane Meyer (Project management)
Project description
Initially, a conception phase for the planned study is funded by the BMBF. The aim of the conception phase is to develop a participatory study concept with the practice partners who carry out the intervention to be evaluated (FREI DAY) and with the target groups of the intervention (teachers and pupils). The aims of the planned study are (1) to evaluate the implementation, (2) to evaluate the structural development effects as well as the health and sustainability effects of FREI DAY (link to a video of the Bredenbeck elementary school). FREI DAY is a whole school approach or a multicomponent/multilevel intervention with integration of school and community. It aims to ensure that the school and students pursue the Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) defined by the United Nations (UN) in a targeted manner through project work. Using participatory and empowering formats, the individual/collective resilience and responsibility of adolescents in particular is promoted in schools so that they can effectively shape the upcoming transformation towards ecologically sustainable, socially just and health-promoting lifestyles and living conditions. The planned design is a multi-level and longitudinal study (controlled before-and-after). A mixed-methods approach and the integration of participatory research methods (e.g. photovoice/reflective photography) will be implemented. The target sample is: >40 schools in which >40 school administrators are nested as well as >400 teachers, >2,000 pupils and >400 key school personnel. Planned analysis methods are: Difference-in-differences (DiD) regression, fixed effects regression, mixed effects regression.
Project management at the MHH
Research assistant
Nicole Heinze
Sponsor
German Pension Insurance
Cooperation with
University of Lübeck
The ReNaApp project was concerned with increasing the long-term effects of oncological rehabilitation for breast cancer through an aftercare app. In the project, breast cancer patients were to be supported and motivated in their intentions and their implementation after a rehabilitation stay by means of an aftercare app. This further development of the "New Credo" aftercare concept was tested and evaluated in oncological rehabilitation.
Project management
Prof. Ulla Walter
Research assistant
Julia Feesche
Project funding
MWK
Aim of the project
The research project builds on the ongoing interdisciplinary research project "Everyday integrated support of children's educational processes in inclusive daycare centers" (KoAkiK) and aims to sustainably implement the contents of the further qualification concept and to support and expand the development of forms of process support for the existing structures of professional cooperation and professional reflection in the daycare centers.
Project team
Representatives from the fields of developmental psychology, inclusive education, didactics and public health
Leibniz Universität Hannover, Institute for Special Needs Education and
Hannover Medical School, Institute of Epidemiology, Social Medicine and Public Health Research
Heike Wadepohl
Katja Mackowiak
Michael Lichtblau
Rolf Werning
Claudia Schomaker
Ulla Walter
Publications
Feesche J, Kula A, Walter U (2022). Handout for training module 4 Everyday integrated promotion of health and resilience. In: Hormann K, Lichtblau M (eds.). Professionals and children in dialog. Practical volume on cognitively activating interaction design in everyday daycare. Beltz Juventa, Weinheim. S. 62-73
Walter U, Feesche J, Heinze N, Kula A (2022). Learning support and cognitive activation in health and resilience promotion. In: Schomaker C, Wadepohl H (Eds.). Professionals and children in dialog. In-depth volume on cognitively activating interaction design in everyday daycare. Beltz Juventa, Weinheim. S. 110-133
Heinze NR, Feesche J, Kula A, Walter U (2021). Health-promoting interaction design in everyday daycare. In: Mackowiak K, Wadepohl H, Beckerle C (eds.). Designing interactions in everyday daycare - basics and suggestions for practice. Verlag W. Kohlhammer, Stuttgart. S. 130-149
Mackowiak K, Kula A, Brunemund L, Walter U (2020). Promotion of social-cognitive problem-solving strategies of preschool children - First results of the joint project KoAkiK. Early Education, 9 (3), 110-117. doi.org/10.1026/2191-9186/a000481
Rothe A, Wadepohl H, Disep L, Mai M, Bethke C, Feesche J, Hormann K & Kula A (2020). "A dialectic stance": Possibilities of mixed-methods designs for capturing professionalism - using videographic approaches to learning-supporting professional-child interactions. In: Bloch B, Kluge L, Tran HM, Zehbe K (eds.): Pädagogik der frühen Kindheit im Wandel. Current challenges and realities. Beltz Juventa, Weinheim/Basel. S. 130-147
The aim of the ICE-PfleGesund (Implementation, Coaching and Development) project was to implement a quality and organizational development concept for health promotion and prevention in inpatient care facilities that is independent of the facility and model and to qualify employees (so-called multipliers) and (external) specialist consultants.
In the implementation sub-project, 25 inpatient care facilities nationwide were to be enabled to develop and implement concepts and measures for health promotion and prevention in accordance with the guidelines for prevention in inpatient care facilities pursuant to Section 5 SGB XI. The Verband der Ersatzkassen e.V. (vdek) commissioned various institutions to carry out the project, so that scientists and practice partners jointly developed and tested qualification offers, concepts and CFP measures in inpatient care facilities. Hannover Medical School was responsible for conducting the evaluation in this project.
Project management at the Institute
Prof. Dr. Ulla Walter & Prof. Dr. Marie-Luise Dierks
Research assistants
Dr. Gabriele Seidel
Antje Meyer
Marius Haack
Project sponsor
Federal Center for Health Education (BZgA)
There has been a significant increase in type 2 diabetes (T2DM) in overweight adults in the first half of life in recent decades. The "Take Care" study focused on primary and secondary prevention. The target group was 18-40-year-olds, including women with gestational diabetes, who have rarely been considered in diabetes prevention to date. Increasing their risk awareness offers the opportunity to protect this population group and their children from T2DM and its consequences.
The aim was to determine awareness, sources of information, information needs, access routes and barriers to T2DM in adults in the first half of life. The method used was 16 guided focus groups, of which 6 group discussions were aimed at overweight pregnant women with and without gestational diabetes. The participants were recruited on the basis of a "theoretical sampling", stratified by gender, age, level of education, occupation, risk, region and migration background.
The results can be used to design a national education and communication strategy. The inclusion of particularly vulnerable subgroups provides indications for the (further) development of possible specific strategies.
Project management
Prof. Dr. Ulla Walter
Scientific collaboration
Dr. Dominik Röding
Nicole Heinze
Project funding
Federal Center for Health Education (BZgA)
Based on the WHO program for health promotion, theories and programs for establishing and expanding intersectoral cooperation have been developed and tested worldwide in recent decades. So far, however, only a few overviews of models and evidence of these programs have been available. Against this background, we conducted a scoping review on behalf of the BZgA (duration: 4/2018 to 12/2018). This study focused on the question of empirical findings on the effectiveness and success factors of model/theory-based strategies to promote intersectoral cooperation in lifestyle-related prevention and health promotion. The results were prepared in particular for a broad specialist audience. In addition, recommendations for action were derived from the results for (1) practitioners, (2) providers of prevention projects and (3) for research.
Publications
Quilling E, Babitsch B, Dadaczynski K, Kruse S, Kuchler M, Köckler H, Leimann J, Walter U, Plantz C (2020). Municipal Health Promotion as Part of Urban Health: A Policy Framework for Action. Sustainability, 12, 6685; doi: 10.3390/su12166685
Quilling E, Kruse S, Kuchler M, Leimann J, Walter U (2020). Models of Intersectoral Cooperation in Municipal Health Promotion and Prevention: Findings from a Scoping Review. Sustainability, 12, 6544; doi: 10.3390/su12166544
Walter U, Röding D, Kruse S, Quilling E (2019). Models and evidence of intersectoral cooperation in community-based prevention and health promotion. Final report. National Association of Statutory Health Insurance Funds (ed.), Berlin
Project management
Prof. Dr. Ulla Walter
Research assistants
Julia Feesche
Nicole Heinze
Antje Kula
Project funding
MWK
Joint project
Leibniz University Hannover and Hannover Medical School
Project team
Team Special Educational Psychology (LUH)
Team Inclusive School Development/Pedagogy for Learning Disabilities (LUH)
Team Special Education and Inclusive Didactics (LUH)
Team Institute of Epidemiology, Social Medicine and Public Health Research(MHH)
Selection of participating KiTas that have expressly agreed to be named
KiTa Eldagsen (German Red Cross)
KiTa Völksen (German Red Cross)
KiTa Bredenbeck (German Red Cross)
KiTa Bierbergen (AWO)
Familienzentrum St. Maxlimilian Kolbe (Caritas)
Aims of the project
Skills development/professionalization of educational professionals in the field of learning support and cognitive activation in (inclusive) daycare centers
Research design
Controlled intervention study with waiting control group
Mixed-method design
Longitudinal design
Evaluation
At the level of the professionals (at 2 measurement points: pre/post)
At the level of the children (at 3 measurement points: pre/post/follow-up)
Sustainability
Training of multipliers for the implementation of a further further qualification phase for educational professionals (waiting control group) in close cooperation with the daycare center providers
Project management
Prof. Dr. Ulla Walter
Research assistant
Katrin Volkenand, MPH
Project sponsor
Federal Center for Health Education (BZgA)
The aim of the research project "Systematization of conceptual approaches to the prevention of childhood obesity in living environments (SkAP)" was to compile an overview of prevention approaches with a focus on obesity prevention in the living environments of children and adolescents (0 to 18 years), to identify gaps, needs and requirements for action and to provide the results for the various settings along the prevention chain.
The overall project was implemented by a working group consisting of a network of 8 university partners. The working group was divided into two core groups. Each member of the core group worked on one of the lifeworlds of family, daycare center, school and community, so that each lifeworld was covered by a tandem (one member of core group 1 and one member of core group 2).
The respective leaders at the location (Table 1) were supported by research assistants.
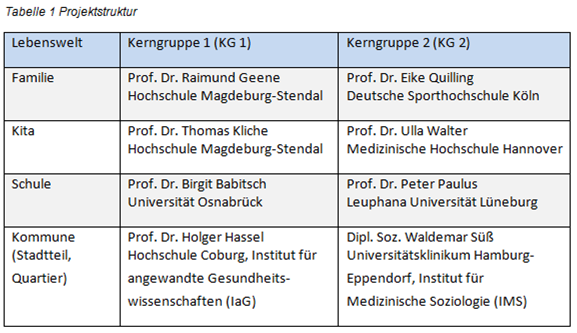
The sub-projects were processed according to a uniform procedure agreed with the overall group. The entire research project was essentially divided into three methodological work phases:
1. catalog of criteria for the description of conceptual approaches to the universal prevention of childhood obesity
- Systematic compilation of criteria catalogs for universal prevention (focus: overweight) in childhood and adolescence in the different lifeworlds and identification of generic and lifeworld-specific description criteria.
- Creation of a common standardized catalog of criteria for the description of interventions for overweight prevention in the lifeworlds of children and adolescents.
- Validation of the criteria catalog by experts
2. systematization of interventions for universal prevention (focus: overweight) in childhood and adolescence:
- Criteria-based identification of interventions within the framework of the defined lifeworlds using this criteria catalog
- Description of interventions in the context of the defined lifeworlds based on the list of criteria
3. synthesis, evaluation and presentation of the results:
- Analysis of conceptual approaches to universal prevention (focus on obesity) in childhood and adolescence
- Identification of strengths and development areas of conceptual approaches
- Derivation of recommendations for action to optimize the areas of development
Short report and final report can be found on the website of the Federal Ministry of Health:
Project management
Prof. Dr. Ulla Walter
Research assistants
Dr. Andrea Dehn-Hindenberg
Lisa Schauermann
Jan Philip Weber
Katrin Volkenand
Project sponsor
Federal Center for Health Education (BZgA)
Project participants
Institute of Epidemiology, Social Medicine and Public Health Research, MHH
Gesellschaft für Beratung Bildung Innovation (BBI)
Bundesvereinigung Prävention und Gesundheitsförderung (BVPG)
Landesvereinigung für Gesundheit und Akademie für Sozialmedizin Niedersachsen (LVG&AFS)
Gesundheit Berlin-Brandenburg (GesBB)
Focal points
Inventory of existing procedures
Legal basis and QA routine
Background
Quality development in primary prevention and health promotion has been discussed for over two decades. There are now several procedures for quality assurance in prevention and health promotion that have been developed in close cooperation between science and practice, some of which have been tried and tested over many years. Laws and subordinate legal regulations such as decrees, but also recommendations and guidelines form an essential framework for the implementation of health promotion and for the perception of quality development and assurance in the individual settings. These can exist at federal, state and municipal level. Individual cost and/or service providers can also define corresponding framework conditions and specify specific procedures or instruments for quality assurance in their Facilities or Institutions. There was no overview of this until then.
Objectives of the sub-project
- To identify and compile legal regulations and subsequent legal framework conditions that affect health promotion in settings with regard to quality development and assurance at federal, state and, where applicable, local authority level,
- to research and summarize guidelines and recommendations from cost and/or service providers in the settings,
- provide an assessment of the quality routines and
- identify starting points for health promotion.
The following settings were considered: kindergarten/daycare center, school, neighborhood/municipality and senior citizens' and care facilities. Workplace health promotion was excluded.
Project management
Prof. Dr. Ulla Walter
Research assistants
Antje Kula
Corinna Wiedel
Project sponsor
Federal Center for Health Education (BZgA)
Main focus
Systematic review
Physical activity, nutrition and life skills are central fields of action in prevention and health promotion, and integration is considered particularly desirable. While reviews of the individual fields of action are available, little is known about the effects of integrated approaches that combine fields of action. The aim of the systematic review was to provide an overview of studies that cover at least two of the three fields of action mentioned for children and adolescents.
An overview of various approaches was compiled in order to arrive at well-founded statements on the effectiveness of combined interventions in the areas of nutrition, exercise and stress management. Building on this, targeted measures to promote the health of children and young people were developed and implemented.
Project management
Prof. Dr. Gerd Naegele
Dr. Andrea Kuhlmann
Prof. Dr. Ulla Walter
Christiane Patzelt
Research assistants
Christiane Pfefferkorn (Hanover)
Dr. Waldemar Schmidt, Sarah Lüders, Sarah Hampel (Dortmund)
Dr. Annette Franke (Frankfurt/Main)
Client
Municipal Association for Youth and Social Affairs Baden-Württemberg (KVJS)
Institutions
Institute of Epidemiology, Social Medicine and Public Health Research, Hannover Medical School
Institute of Gerontology at TU Dortmund University
The municipal level is the place where changes in the age structure of the population have a concrete impact. With the decline in younger population groups in particular, a shortage of skilled workers is also becoming apparent in the relevant fields of municipal services of general interest, especially for elderly care and nursing care. Demand-oriented professionalization and the further development of training structures, in particular the academization of social professions and non-medical Nursing and health professions, can be seen as a significant opportunity both to better meet the future design tasks and to increase the attractiveness of the occupational fields in elderly care and care for the elderly and thus to constructively counter the impending shortage of skilled workers. There were no assumptions regarding the need for non-medical specialists with academic qualifications in elderly care and nursing care for the elderly for the federal state of Baden-Württemberg. The development and review of corresponding demand figures as well as the derivation of future development perspectives for Baden-Württemberg should therefore be the subject of a data-based expertise, whereby requirements resulting from regional differences in particular should be taken into account.
Procedure and methods
1. preparation of the current state of research on the qualification of academic specialists in geriatric work, geriatric care and geriatric nursing (national and international professional and legal development)
2. processing and analysis of demographic and socio-political developments including current legislation (federal and state regulations) with an influence on the need for non-medical academic professions in geriatric work, geriatric care and geriatric nursing in Baden-Württemberg;
3. determination and review of the quantitative demand for non-medical academic professions in geriatric work, geriatric care and geriatric nursing in Baden-Württemberg over the next ten years as well as assessment and exploration of the demand and future developments by experts;
4. research and analysis of non-medical study opportunities in Baden-Württemberg that qualify for the professional field of geriatric work, geriatric care and geriatric nursing
5. derivation of development perspectives for Baden-Württemberg
Publication
Kuhlmann A, Lüders S, Franke A, Hampel S, Naegele G, Schmidt W, Patzelt C, Pfefferkorn C, Walter U (2013). Staffing requirements in elderly care and nursing care in Baden-Württemberg. Expertise taking into account the need for non-medical specialists with academic qualifications. Kommunalverband Jugend und Soziales Baden-Württemberg (ed.).
Project management
Prof. Dr. Ulla Walter
Prof. Dr. Gerd Naegele
Prof. Dr. Nils Schneider
Research assistants
Christiane Patzelt
Hürrem Tezcan-Güntekin
Client
Ministry of Labor and Social Affairs, Family, Women and Senior Citizens Baden-Württemberg
Institutions
Institute of Epidemiology, Social Medicine and Public Health Research, MHH
Institute of Gerontology at the TU Dortmund University
In Baden-Württemberg, the geriatrics concept was revised at the time. The aim was to take stock of the existing structures in health-related care and derive scientifically sound recommendations for the future-oriented and needs-based further development of geriatric care. The research assignment focused on the areas of outpatient geriatric/gerontopsychiatric care and outpatient geriatric rehabilitation. The focus was on structural reform requirements in this area. The study aimed to provide a scientific opinion on the current draft of the new geriatrics concept. In addition to expert workshops and expert interviews, the review and evaluation of available population and prevalence data, the development of low-threshold demand figures for selected areas of care and the review of national and international literature, model projects and recommendations were carried out.
Publication
Walter U, Naegele G, Patzelt C, Tezcan-Güntekin H, Lupp K, Gieseking A (2013) Geriatrics concept for Baden-Württemberg - current situation and requirements for outpatient care and future-oriented further development. Scientific expertise commissioned by the Baden-Württemberg Ministry of Labor, Social Affairs, Family, Women and Senior Citizens.
Project management
Dr. Maren Dreier
Application
Dr. Miriam Gerlich
Research assistants
Mareike Behmann
Silke Kramer
Project sponsor
University internal performance funding (HiLF)
Cooperation partner
PD Dr. Andreas Schäfer, Clinical Department of Cardiology and Angiology, MHH
When an acute myocardial infarction occurs, only a minority of patients reach the hospital within an optimal time window for treatment. The late request for external help is largely due to the subjective decision-making behavior of those affected. Perception and interpretation of the symptoms and the conclusions drawn from them play a role here. The aim of the submitted project was to investigate various coping strategies for acute myocardial infarction symptoms in greater depth. In addition to emotional and cognitive factors, social and care-related contexts were also to be taken into account.
Qualitative guided interviews were conducted with a total of 19 patients with a first acute myocardial infarction after overcoming the critical state of health. The transcribed interviews were analyzed using content analysis. The qualitative analyses were supplemented by basic medical information from the medical records.
The results were intended to contribute to optimizing the start of treatment in the event of an acute event, to shortening the prehospital period and to the care of patients with an increased risk of myocardial infarction.
Project management
Prof. Dr. Ulla Walter
Prof. Dr. Marie-Luise Dierks
Research assistants
Dr. Maren Dreier
Dr. Gabriele Seidel
Birgit Borutta
Inga Kreusel
Project sponsor
Federal Center for Health Education (BZgA)
As part of the National Cancer Plan, the Federal Ministry of Health (BMG) promoted the informed decision of eligible citizens for or against participation in cancer screening examinations. High-quality information on this topic was to be made available via the health portals for women's and men's health of the Federal Center for Health Education (BZgA), among others. In order to identify and evaluate the information materials, the Institute of Epidemiology, Social Medicine and Public Health Research at Hannover Medical School together with the Freiburg University of Education, in close cooperation with the BZgA and the BMG, carried out a research project on behalf of the BZgA from 2008 onwards, which was divided into several phases:
Phase III (duration 2011-2012) - "Promoting the informed decision for early cancer detection - Phase III"
In Phase III, the focus was on websites for colorectal cancer screening. Based on a systematic search, additional quality criteria for information on the Internet were researched and these aspects were added to the list of criteria. Websites with information on colorectal cancer screening were identified and evaluated from an expert perspective using the standardized list of criteria and from a user perspective using focus groups. Users from educationally disadvantaged population groups were also included. A subsequent workshop was held to re-registration the results from phases II and III to the creators of the print materials and websites.
Project management
Prof. Dr. Ulla Walter
Staff members
Birgit Borutta
Stephanie Minne
Project sponsor
Federal Center for Health Education (BZgA)
Institutions
Endowed Chair "Prevention and Rehabilitation in Systems and Health Care Research", MHH
Institute of Epidemiology, Social Medicine and Public Health Research, MHH
Ludwigs-Maximilians-Universität München (LMU), Chair of General Pedagogy and Educational Research
Cooperation partner
Federal Center for Health Education (BZgA)
The project "Parental Competence: Understanding and Operationalization in a Multidisciplinary Perspective" was a cooperation project with the Federal Centre for Health Education and the Chair of General Education and Educational Research at the Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich. The aim was to gain an overview of what is understood by "parenting skills" in the various specialist disciplines (in particular health, education and social sciences) and which approaches exist for defining and measuring parenting skills in order to be able to concretize them conceptually. The aim was to show which skills parents need to be able to adequately promote the development and health of children. Special attention was paid to the question of whether "health-related" skills could be identified in a narrower sense, i.e. skills that parents need in relation to the health promotion and prevention of their children. The focus here was on the promotion of children's health and development in the first years of life (0-6). With regard to the tasks of the BZgA in health promotion and for the planning of future interventions, the question also arose as to what contribution the BZgA can make to promote health and development-relevant skills in parents. The research project was based on a systematic literature review of the state of the art in science and practice.
Project management
Prof. Dr. Ulla Walter
Research assistants
Anke Bramesfeld
Manuela Krieck
Carsten Ungewitter
Project sponsor
Federal Center for Health Education
Project management
Prof. Dr. Ulla Walter
Prof. Dr. Rolf Werning
Prof. Michael Urban
Research assistants
Elena Sterdt
Silke Kramer
Natalie Pape
Project sponsor
Lower Saxony Institute for Early Childhood Education and Development (nifbe)
Lower Saxony Ministry of Science and Culture
Institutions
Institute of Epidemiology, Social Medicine and Public Health Research, MHH
Institute for Special Education, Leibniz Universität Hannover
Cooperation partners
Federal Center for Health Education (BZgA)
University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf (UKE)
German Sport University Cologne
The research project used a mixed-methods design to investigate the relationship between family-related determinants, systematic physical activity concepts in kindergartens and daycare centers and the physical activity behavior, health resources and peer interactions of preschool children. For this purpose, a survey of (systematic) physical activity concepts and structures in kindergartens in Lower Saxony (complete survey: N=4,114) (study module I), a survey of children (N=400) and parents (N=400) in kindergartens (N=40) with or without a systematic physical activity concept (study module II) and ethnographic case studies with children (N=16) (study module III) were conducted. The three study modules were mutually interrelated and made it possible to further detail the respective research results or to place them in a more comprehensive context.
Project management
Prof. Dr. Ulla Walter
Research assistants
Manuela Krieck
Carsten Ungewitter
Project sponsor
Federal Center for Health Education (BZgA)
Project management
Prof. Dr. Ulla Walter
Prof. Dr. Marie-Luise Dierks
Prof. Dr. Rolf Werning
Dr. Michael Urban
Research assistants
Elena Sterdt
Roswitha Stöcker
Project sponsor
Lower Saxony Ministry of Science and Culture
Lower Saxony Institute for Early Childhood Education and Development (nifbe)
Institutions
Endowed Chair "Prevention and Rehabilitation in Systems and Health Care Research", MHH
Institute of Epidemiology, Social Medicine and Public Health Research, MHH
Institute for Special Education, Leibniz Universität Hannover
Cooperation partners
Research Institute of Child Nutrition Dortmund (FKE)
Federal Center for Health Education (BZgA)
University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf (UKE)
In the joint project of the Institute for Special Education at Leibniz University Hannover and the Institute of Epidemiology, Social Medicine and Public Health Research at Hannover Medical School, the subjective constructions of socially disadvantaged children with and without a migration background, their parents and educators on the topic of health with a focus on nutrition and exercise were to be researched in a differentiated manner.
To this end, a primarily qualitative research design was chosen, which was two-phase and multi-perspective. Access to the research field was chosen via the institutional context of the kindergartens and was carried out in the form of an online survey (full survey in the greater Hanover area) and focused group discussions with educators in ten Facilities or Institutions. In the second research phase, a more in-depth study and broadening of perspectives took place in four kindergartens. In particular, the genesis of children's ideas about health was explored using symbolic doll interviews.
At the same time, episodic interviews aimed to include the corresponding ideas and subjective constructs of parents and nursery teachers as the most important reference persons in the microsystems of family and nursery school who moderate children's development. In addition, nutrition and exercise diaries and shopping lists were used to support or contrast the information provided by the interviewees and compare it with expert recommendations (Research Institute of Child Nutrition Dortmud (FKE), American College of Sports Medicine (ACSM), WHO).
The aim was to gain insights into the children's lifeworld development contexts by interlinking the study results and to identify difficulties in fitting in issues of health education and promotion (focus on nutrition and exercise). These results are used as a basis for the target group-oriented design of health concepts (focus on nutrition and exercise) as well as obesity prevention and intervention measures in health education (focus on nutrition and exercise) in the preschool sector. Practical and transfer processes were directly connectable.
Project management
Prof. Dr. Ulla Walter
Research assistants
Martina Plaumann
Madlen Trenker
Project sponsor
Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF)
Collaborative partners
University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf (UKE)
Federal Centre for Health Education (BZgA)
Cooperation partners
Landesvereinigung für Gesundheit Niedersachsen and Akademie für Sozialmedizin e.V.,
Bavarian State Office for Health and Food Safety (LGL) ,
German Society for Social Medicine and Prevention (DGSMP)
The objectives of the project were to publicize the results and findings of the BMBF funding priority "Prevention research", to further develop prevention research and to ensure the sustainable transfer of its results into practice. To this end, the BMBF-funded prevention projects were networked with each other, their results were prepared for science, practice and decision-makers and made known in a bundled form through targeted publications. In order to strengthen prevention research in the long term, its working structures in the Federal Republic of Germany were supported and expanded.
To this end, the project conducted a survey of implementation experience and support needs among German prevention research and its cooperation partners. It presented the BMBF's prevention projects on a website and summarized their most important results in anthologies on the fundamentals of prevention research. These illustrated the knowledge gained from the projects, examined the experiences with practical transfer, summarized the status of research methods and compiled measurement instruments for evaluation and quality assurance. Newsletters and specialist conferences informed relevant target groups about the status, added value and implementation possibilities of prevention and health promotion. In cooperation with leading national and international professional associations, working groups were set up or expanded.
Project management
Prof. Dr. Ulla Walter
PD Dr. Christian Krauth
Research assistants
Sebastian Liersch
Irmtraud Windel
Mustapha Sayed
Dr. Susanne Bisson
Project sponsor
Federal Ministry of Education and Research
Cooperation partner
Lower Saxony State Association for Health and Academy for Social Medicine
The development of organizations is essential for the promotion of health in settings. The explorative study was intended to provide information on the extent to which the organizational intervention "Gesund leben lernen" can lead schools to sustainable changes with regard to a health-promoting orientation and what costs are incurred for the introduction in schools. "Gesund leben lernen" supported schools in the introduction of health management with the help of school coaches. In addition to setting up steering committees and health circles, goals and measures were defined, prioritized and operationalized as part of participatory quality development and evaluation. The strategic management instrument of the Balanced Scorecard was used to support this. As part of the research project, the extent to which this is suitable as a management and evaluation tool in schools was evaluated. The aim was also to create a key performance indicator toolbox that would allow schools to independently monitor the achievement of their objectives and organizational changes.
Further information can be found on the website of the State Association for Health and Academy for Lower Saxony:
Project management
Prof. Dr. Ulla Walter
Prof. Dr. Marie-Luise Dierks
Research assistants
Birgit Borutta
Dr. Maren Dreier
Inga Kreusel
Silke Kramer
Dr. Gabriele Seidel
Project sponsor
Federal Center for Health Education (BZgA)
As part of the National Cancer Plan, the Federal Ministry of Health (BMG) promoted the informed decision of eligible citizens for or against participation in cancer screening examinations. High-quality information on this topic was to be made available via the health portals for women's and men's health of the Federal Center for Health Education (BZgA), among others. In order to identify and evaluate the information materials, the Institute of Epidemiology, Social Medicine and Public Health Research at Hannover Medical School together with the Freiburg University of Education, in close cooperation with the BZgA and the BMG, has been conducting a research project on behalf of the BZgA since 2008, which is divided into several phases:
Phase II (duration 2010) - "Promoting informed decision-making for early cancer detection - Phase II"
The aim of Phase II was the systematic evaluation of health information using the example of screening colonoscopy. After identifying relevant print media, these were analyzed using a new list of criteria developed according to the criteria of evidence-based patient information. The results of the evidence researched in Phase I were used to a large extent for this purpose. In addition to this expert-based evaluation, selected health information was also evaluated by users for comprehensibility and effectiveness in group discussions. The development of the list of criteria was accompanied by experts and the study results were discussed with the accompanying expert panel. This expert discussion resulted in the Phase III project.
Project management
Prof. Dr. Ulla Walter
Prof. Dr. Eva Hummers-Pradier
PD Dr. Christian Krauth
Research assistants
Bernhilde Deitermann
Christiane Patzelt
Jeanett Radisch
Anna Nickel
Jona Stahmeyer
Dr. Gudrun Theile
Susanne Heim
Dr. Guido Schmiemann
Project sponsor
Federal Ministry of Education and Research, funding priority "Prevention research"
Institutions
Institute of Epidemiology, Social Medicine and Public Health Research, MHH
Institute of General Medicine, MHH
Cooperation partners
AOK Lower Saxony
Federal Centre for Health Education (BZgA)
Medical Association of Lower Saxony
Prof. Dr. Hein de Vries, Department of Health Education and Health Promotion, Maastricht University
This was an explorative evaluation study in which qualitative and quantitative methods were used. In addition, claims data from a health insurance company were analyzed. The study was dedicated to the systematic further development of target group-oriented access routes. Central questions included how older women and men can be motivated to take preventive measures and which access routes can be used to reach older people with different health risks. These were examined using the example of the preventive home visit. The preventive home visit is a measure of outreach counseling for older people in their home environment with the aim of maintaining an independent lifestyle, promoting health and preventing illness. Preventive home visits have been offered by AOK Niedersachsen in selected regions since 2004.
With the conception and evaluation of an age-group and gender-sensitive written initial information and telephone approach, the target group-oriented addressing, which is often demanded but neglected in research and practice, was taken into account. The flyer developed in a multi-stage process (focus groups, interviews, expert panel) and the target group-specific letter were used to motivate AOK policyholders over the age of 65 to take part in preventive home visits. Two access routes were tested and evaluated in terms of their effectiveness and cost-effectiveness via central Facilities or Institutions in the healthcare system (telephone consultation by health insurance company, face-to-face consultation in the GP practice). The study was carried out in selected regions of the large cities of Hanover and Braunschweig and in the small towns of Verden and Delmenhorst. The results led to recommendations that were discussed at a scientific expert conference and concretized in terms of their implementation for care practice with representatives from practice and politics.
Overall, the study comprised three parts:
A Development and optimization of a target group-oriented written information and telephone approach
B Testing and evaluation of access routes
C Development of recommendations and their transfer to science and care practice
Publications
- Patzelt C, Deitermann B, Heim S, Krauth C, Theile G, Hummers-Pradier E, Walter U (2012): The preventive home visit as an outreach prevention measure - accessibility of vulnerable groups. Joint congress of the DGMS and ESHMS: Health inequality across the life course, 30.08.-01.09.2012, Hanover
- Reaching older people in a targeted manner - effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of access routes using the example of preventive home visits. In: BZgA (ed.): Using the results of prevention research. 14 examples from the BMBF funding priority. Prevention projects for older people
- Patzelt C, Deitermann B, Heim S, Krauth C, Theile G, Hummers-Pradier E, Walter U (2012): How can older people be motivated to make use of preventive home visits? Public Health Forum 74
- Patzelt C, Deitermann B, Heim S, Krauth C, Theile G, Walter U (2012): Targeting older people with preventive measures - addressing and reaching them via different access routes, 11th German Congress for Health Services Research and 4th National Prevention Congress: Prevention and Care 2012 for Health 2030. A challenge for medicine and dentistry. 27.09.-29.09.2012, Dresden
- Patzelt C, Stahmeyer JT, Deitermann B, Heim S, Lupp K, Theile G, Hummers-Pradier E, Krauth C, Walter U (2012): Reaching older people in a targeted manner - target group-specific approach via two access routes using the example of the preventive home visit. Joint Gerontology and Geriatrics Congress: Ageing research: transnational and translational, 12.09.15.09.2012, Bonn
- Patzelt C, Stahmeyer JT, Deitermann B, Heim S, Lupp K, Theile G, Hummers-Pradier E, Krauth C, Walter U (2012): GP versus health insurance - effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of access pathways using the example of the preventive home visit. Annual scientific conference of the DGSMP: Health economics versus social medicine. How much economization can a solidary health system tolerate? 12.09.-14.09.2012, Essen
- Walter U, Patzelt C, Deitermann B, Heim S, Schmiemann G, Theile G, Krauth C, Hummers-Pradier E (2011): Reaching older people in a targeted way (AeGE) - effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of access routes using the example of the preventive home visit. Lower Saxony Medical Journal 6, 69-70
- Deitermann B, Patzelt C, Heim S, Krauth C, Theile G, Hummers-Pradier E, Walter U (2011): Successful prevention needs a gender-appropriate approach. Public Health Forum 19, Issue 71, 9-10
- Patzelt C, Deitermann B, Radisch J, Heim S, Schmiemann G, Theile G, Nickel A, Hummers-Pradier E, Krauth C, Walter U (2010) Would this be something for you? Further development of a target group-oriented approach for an outreach prevention measure in old age. Healthcare 2010; 72: 614
- Deitermann B, Patzelt C, Radisch J, Heim S, Schmiemann G, Theile G, Nickel A, Hummers-Pradier E, Krauth C, Walter U (2010): "Reaching older people in a targeted way" - Evaluation of different access routes using the example of the preventive home visit. Journal of Gerontology and Geriatrics; 1: 119-120
- Heim S, Lingner H, Deitermann B, Patzelt C, Krauth C, Walter U , Hummers-Pradier E, Theile G (2010): Mapping procedures as an evaluation method for focus groups in prevention and health services research. Monitor Health Services Research; 53: FV 38
- Theile G, Heim S, Patzelt C, Deitermann B, Walter U, Hummers-Pradier E. (2010): Preventive home visits - who is actually interested in them? Section 23.4. in: Kirch W, Middeke M, Rychlik R (eds.). Aspects of prevention, Thieme, Stuttgart - New York, 187-189
- Heim S, Theile G, Deitermann B, Patzelt C, Hummers-Pradier, E, Walter U (2009): Who wants a preventive home visit? Older people and their wishes regarding preventive services. Z Allg Med, special issue DEGAM/DKVF 2009; W323, 151-152
- Deitermann B, Patzelt C, Bisson S, Heim S, Theile G, Hummers-Pradier E, Walter U (2009): Older people as a target group for research: possibilities and limitations of focus groups with people over 65 years of age, Gesundheitswesen; 71: A167
- Patzelt C, Deitermann B, Bisson S, Heim S, Theile G, Hummers-Pradier E, Walter U (2009): Understanding of health and utilization of preventive services from the perspective of older people. Public Health; 71: A18
Project management
Prof. Dr. Ulla Walter
Prof. Dr. Marie-Luise Dierks
Research assistants
Birgit Borutta
Dr. Maren Dreier
Silke Kramer
Inga Kreusel
Dr. Gabriele Seidel
Ursula Schlanstedt-Jahn
Project sponsor
Federal Center for Health Education (BZgA)
As part of the National Cancer Plan, the Federal Ministry of Health (BMG) promoted the informed decision of eligible citizens for or against participation in cancer screening examinations. High-quality information on this topic was to be made available via the health portals for women's and men's health of the Federal Center for Health Education (BZgA), among others. In order to identify and evaluate the information materials, the Institute of Epidemiology, Social Medicine and Public Health Research at Hannover Medical School together with the Freiburg University of Education, in close cooperation with the BZgA and the BMG, carried out a research project on behalf of the BZgA since 2008, which was divided into several phases:
Phase I (duration 2008-09) - "Development of a concept to improve the utilization of early detection examinations according to §25 SGB V"
included a systematic comparison of screening examinations in accordance with Section 25 SGB V with the aim of prioritizing them for the preparation of evidence-based information. To this end, an initial analysis of the statutory health check-ups was carried out using defined criteria with the aim of selecting screening procedures for targeted interventions to promote informed utilization. The selection of procedures (prioritization) during an expert workshop formed the conclusion of Phase I. Four target diseases were selected: Breast cancer, cervical cancer, colorectal cancer and cardiovascular disease. The closer connection to the goals of the National Cancer Plan led to a further focus on cancer screening examinations (KFU). It was decided to carry out further research activities on the target disease of colorectal cancer and the screening colonoscopy procedure, which has been available to people with statutory health insurance in Germany since October 2002.
Project management
Prof. Dr. Ulla Walter
PD Dr. Christian Krauth
Dr. Markus Röbl
Research assistants
Dr. Susanne Bisson
Dr. Vicky Henze
Sebastian Liersch
Elena Sterdt
Project sponsor
Federal Ministry of Education and Research
Cooperation partners
University Children's Hospital Göttingen
Allgemeiner Sport-Club Göttingen von 1846(ASC46) e.V.
Ärztekammer Niedersachsen
Gesundheitsamt für die Stadt und den Landkreis Göttingen
Institute for Sports Science at the University of Göttingen
Pädagogisches Seminar der Universität Göttingen
Schools
Lohbergschule
Wilhelm-Henneberg-Schule
Hölty-Schule
Heinrich-Grupe-Schule in Rosdorf
Brüder-Grimm-Schule
Albanischule
Physical inactivity and overweight/obesity have increased among children and adolescents over the past decade. They represent a significant risk factor for chronic diseases. The promotion of physical activity is already important in the first decade of life. Daily physical education in elementary school is an important approach due to the complete accessibility of children. The "fit for pisa" intervention took up the frequently raised demands for daily, quality-managed, curriculum-structured and standardized physical education by professionally qualified teachers and implemented them in 6 schools.
The aim of the study was to evaluate the effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of daily physical education in a longitudinal and cross-sectional approach. It was intended to provide information on the extent to which daily physical education has a long-term effect on the health and physical activity behavior of pupils, even after the intervention has ended, and to what extent children with increased risk factors benefit from the offer. The results of the overall project led to recommendations for the introduction of additional PE lessons in elementary school, tools for quality assurance and suggestions for optimizing the framework guidelines and the content of the curriculum for PE lessons in grades 1 to 4 of elementary school.
The study examined sustainability one and two years after completion of the intervention with regard to health and education-related effects. Gender-specific and socio-economic variables were specifically taken into account and evaluated. For the first time, an economic evaluation provided information on short and long-term savings potential in terms of follow-up costs.